Exploration of Succinimide Derivative as a Multi-Target, Anti-Diabetic Agent: In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches
- PMID: 36838577
- PMCID: PMC9964140
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28041589
Exploration of Succinimide Derivative as a Multi-Target, Anti-Diabetic Agent: In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches
Abstract
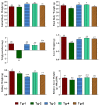
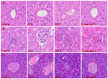
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is counted among one of the leading challenges in the recent era, and it is a life-threatening disorder. Compound 4-hydroxy 3-methoxy phenylacetone (compound 1) was previously isolated from Polygonum aviculare. This compound was reacted with N-benzylmaleimide to synthesize the targeted compound 3. The purpose of this research is to exhibit our developed compound 3's ability to concurrently inhibit many targets that are responsible for hyperglycemia. Compound 3 was capable of inhibiting α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 B. Even so, outstanding in vitro inhibition was shown by the compound against dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) with an IC50 value of 0.07 µM. Additionally, by using DPPH in the antioxidant activity, it exhibited good antioxidant potential. Similarly, in the in vivo activity, the experimental mice proved to be safe by treatment with compound 3. After 21 days of examination, the compound 3 activity pattern was found to be effective in experimental mice. Compound 3 decreased the excess peak of total triglycerides, total cholesterol, AST, ALT, ALP, LDL, BUN, and creatinine in the STZ-induced diabetic mice. Likewise, the histopathology of the kidneys, liver, and pancreas of the treated animals was also evaluated. Overall, the succinimde moiety, such as compound 3, can affect several targets simultaneously, and, finally, we were successful in synthesizing a multi-targeted preclinical therapy.
Keywords: acute toxicity; antioxidant; diabetes; histopathology; succinimide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors affirm that there are no conflicts of interest and that our revised manuscript, now titled “Design, synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of succinimide derivative as multi target inhibitor of α-amylase, α-glucosidase, DPP4 and PTP-1 B for the treatment of type-II diabetes” has not been published or is not currently being considered for publishing in any journal, seminar, or conference.
Figures



References
-
- Lawal M., Verma A.K., Umar I.A., Gadanya A.M., Umar B., Yahaya N., Auwal B. Analysis of New Potent Anti-Diabetic Molecules from Phytochemicals of PistiaStrateotes with Sglt1 and G6pc Proteins of Homo Sapiens for Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. An In SilicoApproach. Silico Approach IOSR JPBS. 2020;15:59–73.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

