Design of TiO2-Based Hybrid Systems with Multifunctional Properties
- PMID: 36838853
- PMCID: PMC9967613
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28041863
Design of TiO2-Based Hybrid Systems with Multifunctional Properties
Erratum in
-
Correction: Ortelli et al. Design of TiO2-Based Hybrid Systems with Multifunctional Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 1863.Molecules. 2024 Sep 30;29(19):4647. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194647. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407713 Free PMC article.
Abstract
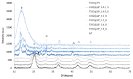
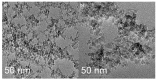
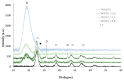
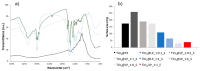
In recent years, multifunctional inorganic-organic hybrid materials have been widely investigated in order to determine their potential synergetic, antagonist, or independent effects in terms of reactivity. The aim of this study was to design and characterize a new hybrid material by coupling well-known photocatalytic TiO2 nanoparticles with a mixture of lipopeptides (LP), to exploit its high binding affinity for metal cations as well as the ability to interact with bacterial membranes and disrupt their integrity. We used both chemical and colloidal synthesis methodologies and investigated how different TiO2:LP weight ratios affected colloidal, physicochemical, and functional properties. We discovered a clear breaking point between TiO2 and LP single-component trends and identified different ranges of applicability by considering different functional properties such as photocatalytic, heavy metal sorption capacity, and antibacterial properties. At low LP contents, the photocatalytic properties of TiO2 are preserved (conversion of organic dye = 99% after 40 min), and the hybrid system can be used in advanced oxidation processes, taking advantage of the additional antimicrobial LP properties. Around the breaking point (TiO2:LP 1:1), the hybrid material preserves the high surface area of TiO2 (specific surface area around 180 m2/g) and demonstrates NOx depletion of up to 100% in 80 min, together with improved adhesion of hybrid antibacterial coating. The last design demonstrated the best results for the concurrent removal of inorganic, organic, and biological pollutants in water/soil remediation applications.
Keywords: antibacterial coating; hybrid system; nano-TiO2; photocatalyst; sodium surfactin; sorption capacity.
Conflict of interest statement
Giovanni Baldi and Valentina Dami was employed by the company Ce.Ri.Col, Colorobbia Consulting S.R.L. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, United Nations. [(accessed on 20 December 2022)]. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda.
-
- Lee S.Y., Park S.J. TiO2 Photocatalyst for Water Treatment Applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013;19:1761–1769. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2013.07.012. - DOI
-
- Ortelli S., Blosi M., Delpivo C., Gardini D., Dondi M., Gualandi I., Tonelli D., Aina V., Fenoglio I., Gandhi A.A., et al. Multiple Approach to Test Nano TiO2 Photo-Activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2014;292:26–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2014.07.006. - DOI
-
- Faccani L., Ortelli S., Blosi M., Costa A.L. Ceramized Fabrics and Their Integration in a Semi-Pilot Plant for the Photodegradation of Water Pollutants. Catalysts. 2021;11:1418. doi: 10.3390/catal11111418. - DOI
-
- Koivisto A.J., Trabucco S., Ravegnani F., Calzolari F., Nicosia A., del Secco B., Altin M., Morabito E., Blosi M., Costa A., et al. Nanosized Titanium Dioxide Particle Emission Potential from a Commercial Indoor Air Purifier Photocatalytic Surface: A Case Study. Open Res. Eur. 2022;2:84. doi: 10.12688/openreseurope.14771.1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

