Curcuma aromatica Salisb. Protects from Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Regulating the Sirt1/HO-1 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 36839166
- PMCID: PMC9964786
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15040808
Curcuma aromatica Salisb. Protects from Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Regulating the Sirt1/HO-1 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
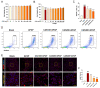
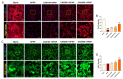
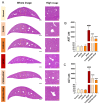
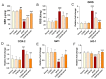
Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose-induced hepatotoxicity reduces the activity of sirtuin-1 (Sirt1) along with heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) and promotes inflammatory responses and oxidative stress. Although the extract of Curcuma aromatica Salisb. (CAS) possesses hepatoprotective properties, scientific evidence on whether CAS prevents hepatotoxicity and the underlying molecular mechanisms are lacking. Here, we hypothesized that CAS ameliorates hepatotoxicity by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress via Sirt1/HO-1 signaling. CAS pretreatment at doses of 200 and 400 μg/mL significantly increased cell viability in APAP-treated primary hepatocytes. The expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) substantially increased after APAP treatment; however, this expression significantly decreased in cells pretreated with 100, 200, and 400 µg/mL CAS. CAS increased Sirt1 and HO-1 levels in APAP-treated hepatocytes in a dose-dependent manner. When CAS was orally administered to mice at doses of 20 or 100 mg/kg for 7 days, the APAP-induced increase in serum aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase levels was inhibited. Moreover, CAS decreased IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β, increased IL-10, suppressed ROS generation, increased glutathione levels, inhibited iNOS and cyclooxygenase-2, and enhanced Sirt1 and HO-1 in the mouse model of APAP-induced hepatotoxicity. These findings suggest that CAS could be used as a natural hepatoprotective drug to treat APAP-induced injury.
Keywords: Curcuma aromatica Salisb.; HO-1; Sirt1; acetaminophen; hepatotoxicity; paracetamol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
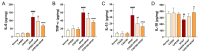
References
-
- Larson A.M., Polson J., Fontana R.J., Davern T.J., Lalani E., Hynan L.S., Reisch J.S., Schiodt F.V., Ostapowicz G., Shakil A.O., et al. Acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: Results of a United States multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology. 2005;42:1364–1372. doi: 10.1002/hep.20948. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reddy K.R., Ellerbe C., Schilsky M., Stravitz R.T., Fontana R.J., Durkalski V., Lee W.M., Acute Liver Failure Study Group Determinants of outcome among patients with acute liver failure listed for liver transplantation in the United States. Liver Transpl. 2016;22:505–515. doi: 10.1002/lt.24347. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

