Beneficial Effects of ε-Viniferin on Obesity and Related Health Alterations
- PMID: 36839286
- PMCID: PMC9963111
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15040928
Beneficial Effects of ε-Viniferin on Obesity and Related Health Alterations
Abstract
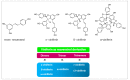
Viniferin is a phenolic compound belonging to the group of stilbenoids. In particular, ε-viniferin is a dimer of resveratrol, found in many plant genders, among which grapes (Vitis vinifera) are a primary source. Due to the fact that ε-viniferin is mainly present in the woody parts of plants, their use as a source of this bioactive compound is a very interesting issue in a circular economy. Both, in vitro studies carried out in pre-adipocytes and mature adipocytes and in vivo studies addressed in mice show that ε-viniferin is able to reduce fat accumulation. Moreover, it prevents the development of some obesity co-morbidities, such as type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemias, hypertension and fatty liver. ε-viniferin can be absorbed orally, but it shows a very low bioavailability. In this scenario, further research on animal models is needed to confirm the effects reported in a great number of studies; to determine which metabolites are involved, including the main one responsible for the biological effects observed and the mechanisms that justify these effects. In a further phase, human studies should be addressed in order to use ε-viniferin as a new tool for obesity management, as a nutraceutical or to be included in functional foods.
Keywords: dyslipidemia; fatty liver; glucose homeostasis; hypertension; obesity; viniferin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bhoyrul S., Lashock J. The physical and fiscal impact of the obesity epidemic: The impact of comorbid conditions on patients and payers. J. Manag. Care Med. 2008;11:10–17.
-
- Fuloria S., Sekar M., Khattulanuar F.S., Gan S.H., Rani N.N.I.M., Ravi S., Subramaniyan V., Jeyabalan S., Begum M.Y., Chidambaram K., et al. Chemistry, Biosynthesis and Pharmacology of Viniferin: Potential Resveratrol-Derived Molecules for New Drug Discovery, Development and Therapy. Molecules. 2022;27:5072. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165072. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

