Low-Protein Formulas with Alpha-Lactalbumin-Enriched or Glycomacropeptide-Reduced Whey: Effects on Growth, Nutrient Intake and Protein Metabolism during Early Infancy: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36839368
- PMCID: PMC9958764
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15041010
Low-Protein Formulas with Alpha-Lactalbumin-Enriched or Glycomacropeptide-Reduced Whey: Effects on Growth, Nutrient Intake and Protein Metabolism during Early Infancy: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Controlled Trial
Abstract
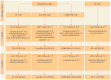
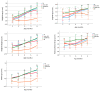
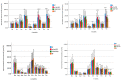
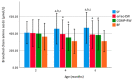
Protein intake is higher in formula-fed than in breast-fed infants during infancy, which may lead to an increased risk of being overweight. Applying alpha-lactalbumin (α-lac)-enriched whey or casein glycomacropeptide (CGMP)-reduced whey to infant formula may enable further reduction of formula protein by improving the amino acid profile. Growth, nutrient intake, and protein metabolites were evaluated in a randomized, prospective, double-blinded intervention trial where term infants received standard formula (SF:2.2 g protein/100 kcal; n = 83) or low-protein formulas with α-lac-enriched whey (α-lac-EW;1.75 g protein/100 kcal; n = 82) or CGMP-reduced whey (CGMP-RW;1.76 g protein/100 kcal; n = 80) from 2 to 6 months. Breast-fed infants (BF; n = 83) served as reference. Except between 4 and 6 months, when weight gain did not differ between α-lac-EW and BF (p = 0.16), weight gain was higher in all formula groups compared to BF. Blood urea nitrogen did not differ between low-protein formula groups and BF during intervention, but was lower than in SF. Essential amino acids were similar or higher in α-lac-EW and CGMP-RW compared to BF. Conclusion: Low-protein formulas enriched with α-lac-enriched or CGMP-reduced whey supports adequate growth, with more similar weight gain in α-lac-enriched formula group and BF, and with metabolic profiles closer to that of BF infants.
Keywords: CGMP; alpha-lactalbumin; amino acids; energetic efficiency; infant formula; infant growth; low protein; obesity; protein metabolism; protein quality.
Conflict of interest statement
Arla Foods Ingredients Group P/S, Viby J, Denmark funded the study and provided the infant formula. The funder had no role in the study design, data collection, analyses, interpretation of data or impact on decision to publish the results. M.L.H., L.N.J., A.S.K. are employees of Arla Foods Ingredients and participated in the work with the final manuscript. B.L. and O.H. have received research grants and honorarium from Arla Foods Ingredients. P.K.Å has received a research honorarium. The authors declare no other conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

