Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome-An Extempore Game of Misfiring with Defense Arsenals
- PMID: 36839482
- PMCID: PMC9964757
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12020210
Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome-An Extempore Game of Misfiring with Defense Arsenals
Abstract
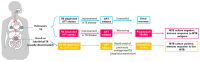
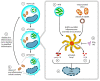
The lethal combination involving TB and HIV, known as "syndemic" diseases, synergistically act upon one another to magnify the disease burden. Individuals on anti-retroviral therapy (ART) are at risk of developing TB-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (TB-IRIS). The underlying inflammatory complication includes the rapid restoration of immune responses following ART, eventually leading to exaggerated inflammatory responses to MTB antigens. TB-IRIS continues to be a cause of morbidity and mortality among HIV/TB coinfected patients initiating ART, and although a significant quantum of knowledge has been acquired on the pathogenesis of IRIS, the underlying pathomechanisms and identification of a sensitive and specific diagnostic marker still remain a grey area of investigation. Here, we reviewed the latest research developments into IRIS immunopathogenesis, and outlined the modalities to prevent and manage strategies for better clinical and diagnostic outcomes for IRIS.
Keywords: ART; HIV; IRIS; biomarkers; inflammation; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2021. [(accessed on 19 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240037021.
-
- Shankar E.M., Vignesh R., Ellegård R., Barathan M., Chong Y.K., Bador M.K., Rukumani D.V., Sabet N.S., Kamarulzaman A., Velu V., et al. HIV-Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Co-Infection: A “danger-Couple Model” of Disease Pathogenesis. Pathog. Dis. 2014;70:110–118. doi: 10.1111/2049-632X.12108. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

