Pathological Features and Genomic Characterization of an Actinobacillus equuli subsp. equuli Bearing Unique Virulence-Associated Genes from an Adult Horse with Pleuropneumonia
- PMID: 36839495
- PMCID: PMC9962156
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12020224
Pathological Features and Genomic Characterization of an Actinobacillus equuli subsp. equuli Bearing Unique Virulence-Associated Genes from an Adult Horse with Pleuropneumonia
Abstract
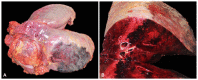
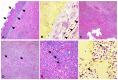
Actinobacillus equuli subsp. equuli is the etiological agent of sleepy foal disease, an acute form of fatal septicemia in newborn foals. A. equuli is commonly found in the mucous membranes of healthy horses' respiratory and alimentary tracts and rarely causes disease in adult horses. In this study, we report a case of a 22-year-old American Paint gelding presenting clinical signs associated with an atypical pattern of pleuropneumonia subjected to necropsy. The gross and histopathological examinations revealed a unilateral fibrinosuppurative and hemorrhagic pleuropneumonia with an infrequent parenchymal distribution and heavy isolation of A. equuli. The whole genome sequence analysis indicated that the isolate shared 95.9% homology with the only other complete genome of A. equuli subsp. equuli available in GenBank. Seven virulence-associated genes specific to the isolate were identified and categorized as iron acquisition proteins, lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and capsule polysaccharides. Moreover, four genes (glf, wbaP, glycosyltransferase family 2 protein, and apxIB) shared higher amino acid similarity with the invasive Actinobacillus spp. than the reference A. equuli subsp. equuli genome. Availability of the whole genome sequence will allow a better characterization of virulence determinants of A. equuli subsp. equuli, which remain largely elusive.
Keywords: Actinobacillus equuli subsp. equuli; equine actinobacillosis; whole genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Complete genome sequence of Actinobacillus equuli subspecies equuli ATCC 19392(T).Stand Genomic Sci. 2015 Jun 7;10:32. doi: 10.1186/s40793-015-0009-x. eCollection 2015. Stand Genomic Sci. 2015. PMID: 26203343 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective study of equine actinobacillosis cases: 1999-2011.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2014 May;26(3):365-375. doi: 10.1177/1040638714531766. Epub 2014 Apr 17. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2014. PMID: 24742921
-
Reclassification of equine isolates previously reported as Actinobacillus equuli, variants of A. equuli, Actinobacillus suis or Bisgaard taxon 11 and proposal of A. equuli subsp. equuli subsp. nov. and A. equuli subsp. haemolyticus subsp. nov.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2002 Sep;52(Pt 5):1569-1576. doi: 10.1099/00207713-52-5-1569. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12361259
-
Revised definition of Actinobacillus sensu stricto isolated from animals. A review with special emphasis on diagnosis.Vet Microbiol. 2004 Mar 26;99(1):13-30. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2003.12.002. Vet Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15019108 Review.
-
The role of RTX toxins in host specificity of animal pathogenic Pasteurellaceae.Vet Microbiol. 2011 Nov 21;153(1-2):51-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.05.018. Epub 2011 May 19. Vet Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21645978 Review.
References
-
- MacInnes J.I. Actinobacillus. Wiley-Blackwell; Ames, IA, USA: 2010.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

