Employing T-Cell Memory to Effectively Target SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36839573
- PMCID: PMC9967959
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12020301
Employing T-Cell Memory to Effectively Target SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
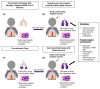
Well-trained T-cell immunity is needed for early viral containment, especially with the help of an ideal vaccine. Although most severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-infected convalescent cases have recovered with the generation of virus-specific memory T cells, some cases have encountered T-cell abnormalities. The emergence of several mutant strains has even threatened the effectiveness of the T-cell immunity that was established with the first-generation vaccines. Currently, the development of next-generation vaccines involves trying several approaches to educate T-cell memory to trigger a broad and fast response that targets several viral proteins. As the shaping of T-cell immunity in its fast and efficient form becomes important, this review discusses several interesting vaccine approaches to effectively employ T-cell memory for efficient viral containment. In addition, some essential facts and future possible consequences of using current vaccines are also highlighted.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; T cells; lung TRM; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Le Bert N., Clapham H.E., Tan A.T., Chia W.N., Tham C.Y.L., Lim J.M., Kunasegaran K., Tan L.W.L., Dutertre C.-A., Shankar N., et al. Highly functional virus-specific cellular immune response in asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Exp. Med. 2021;218:e20202617. doi: 10.1084/jem.20202617. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tan A.T., Linster M., Tan C.W., Le Bert N., Chia W.N., Kunasegaran K., Zhuang Y., Tham C.Y.L., Chia A., Smith G.J., et al. Early induction of functional SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells associates with rapid viral clearance and mild disease in COVID-19 patients. Cell Rep. 2021;34:108728. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108728. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

