T Cell Response to SARS-CoV-2 Coinfection and Comorbidities
- PMID: 36839596
- PMCID: PMC9965203
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12020321
T Cell Response to SARS-CoV-2 Coinfection and Comorbidities
Abstract
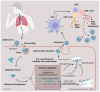
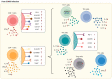
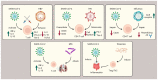
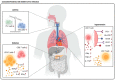
For the past three years, COVID-19 has become an increasing global health issue. Adaptive immune cells, especially T cells, have been extensively investigated in regard to SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, human health and T cell responses are also impacted by many other pathogens and chronic diseases. We have summarized T cell performance during SARS-CoV-2 coinfection with other viruses, bacteria, and parasites. Furthermore, we distinguished if those altered T cell statuses under coinfection would affect their clinical outcomes, such as symptom severity and hospitalization demand. T cell alteration in diabetes, asthma, and hypertension patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection was also investigated in our study. We have summarized whether changes in T cell response influence the clinical outcome during comorbidities.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; T cells; coinfection; comorbidities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vanella G., Capurso G., Burti C., Fanti L., Ricciardiello L., Lino A.S., Boskoski I., Bronswijk M., Tyberg A., Krishna Kumar Nair G., et al. Gastrointestinal mucosal damage in patients with COVID-19 undergoing endoscopy: An international multicentre study. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2021;8:e000578. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2020-000578. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tesoriero J.M., Swain C.E., Pierce J.L., Zamboni L., Wu M., Holtgrave D.R., Gonzalez C.J., Udo T., Morne J.E., Hart-Malloy R., et al. COVID-19 Outcomes Among Persons Living With or Without Diagnosed HIV Infection in New York State. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2037069. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37069. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

