Saponins: Research Progress and Their Potential Role in the Post-COVID-19 Pandemic Era
- PMID: 36839670
- PMCID: PMC9964560
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020348
Saponins: Research Progress and Their Potential Role in the Post-COVID-19 Pandemic Era
Abstract
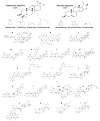
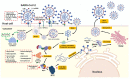
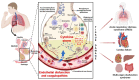
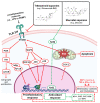
In the post-COVID-19 pandemic era, the new global situation and the limited therapeutic management of the disease make it necessary to take urgent measures in more effective therapies and drug development in order to counteract the negative global impacts caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and its new infectious variants. In this context, plant-derived saponins-glycoside-type compounds constituted from a triterpene or steroidal aglycone and one or more sugar residues-may offer fewer side effects and promising beneficial pharmacological activities. This can then be used for the development of potential therapeutic agents against COVID-19, either as a therapy or as a complement to conventional pharmacological strategies for the treatment of the disease and its prevention. The main objective of this review was to examine the primary and current evidence in regard to the therapeutic potential of plant-derived saponins against the COVID-19 disease. Further, the aim was to also focus on those studies that highlight the potential use of saponins as a treatment against SARS-CoV-2. Saponins are antiviral agents that inhibit different pharmacological targets of the virus, as well as exhibit anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic activity in relieving symptoms and clinical complications related to the disease. In addition, saponins also possess immunostimulatory effects, which improve the efficacy and safety of vaccines for prolonging immunogenicity against SARS-CoV-2 and its infectious variants.
Keywords: COVID-19; adjuvant; anti-inflammatory; antithrombotic; antiviral; immunostimulatory; saponin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular Insights of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Molecular Treatments.Curr Mol Med. 2022;22(7):621-639. doi: 10.2174/1566524021666211013121831. Curr Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34645374 Review.
-
Testing the efficacy and safety of BIO101, for the prevention of respiratory deterioration, in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (COVA study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 11;22(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04998-5. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33430924 Free PMC article.
-
Molnupiravir and Its Antiviral Activity Against COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 4;13:855496. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.855496. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35444647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on the Effectivity of the Current COVID-19 Drugs and Vaccines: Are They Really Working Against the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Variants?Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. 2021;8(3):186-193. doi: 10.1007/s40588-021-00172-w. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34249605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TMPRSS2 and RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Are Effective Targets of Therapeutic Intervention for Treatment of COVID-19 Caused by SARS-CoV-2 Variants (B.1.1.7 and B.1.351).Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Sep 3;9(1):e0047221. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00472-21. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34378968 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Triterpenoidal Saponins from the Leaves of Aster koraiensis Offer Inhibitory Activities against SARS-CoV-2.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 19;13(2):303. doi: 10.3390/plants13020303. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38276760 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological and Toxicological Assessment of Triterpenoid Saponins Bearing Lewis-X- and QS-21-Based Trisaccharides.Chemistry. 2025 May 19;31(28):e202500994. doi: 10.1002/chem.202500994. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Chemistry. 2025. PMID: 40192644 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical synergies in BK002: advanced molecular docking insights for targeted prostate cancer therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 17;16:1504618. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1504618. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40034825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspectives on Saponins: Food Functionality and Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 31;24(17):13538. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713538. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements and challenges in pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic research on the traditional Chinese medicine saponins: a comprehensive review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 7;15:1393409. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1393409. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38774213 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oleszek M., Oleszek W. Saponins in Food. In: Xiao J., Sarker S.D., Asakawa Y., editors. Handbook of Dietary Phytochemicals. 1st ed. Volume 1. Springer; Singapore: 2019. pp. 1–40. - DOI
-
- Osbourn A. Saponins and plant defence—a soap story. Trends Plant Sci. 1996;1:4–9. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(96)80016-1. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

