Interactions between DMPC Model Membranes, the Drug Naproxen, and the Saponin β-Aescin
- PMID: 36839701
- PMCID: PMC9960855
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020379
Interactions between DMPC Model Membranes, the Drug Naproxen, and the Saponin β-Aescin
Abstract
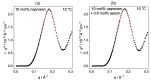
In this study, the interplay among the phospholipid 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC) as a model membrane, the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug naproxen, and the saponin β-aescin are investigated. The naproxen amount was fixed to 10 mol%, and the saponin amount varies from 0.0 to 1.0 mol%. Both substances are common ingredients in pharmaceutics; therefore, it is important to obtain deeper knowledge of their impact on lipid membranes. The size and properties of the DMPC model membrane upon naproxen and aescin addition were characterized with differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS, WAXS), and photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS) in a temperature-dependent study. The interaction of all substances was dependent on the lipid phase state, which itself depends on the lipid's main phase transition temperature Tm. The incorporation of naproxen and aescin distorted the lipid membrane structure and lowers Tm. Below Tm, the DMPC-naproxen-aescin mixtures showed a vesicle structure, and the insertion of naproxen and aescin influenced neither the lipid chain-chain correlation distance nor the membrane thickness. Above Tm, the insertion of both molecules instead induced the formation of correlated bilayers and a decrease in the chain-chain correlation distance. The presented data clearly confirm the interaction of naproxen and aescin with DMPC model membranes. Moreover, the incorporation of both additives into the model membranes is evidenced.
Keywords: DMPC; DSC; PCS; SAXS; WAXS; naproxen; nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug; saponin; small unilamellar vesicles (SUVs); β-aescin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures












References
-
- Kiselev M.A. Methods for Lipid Nanostructure Investigation at Neutron and Synchrotron Sources. Phys. Part. Nucl. 2011;42:302–331. doi: 10.1134/S1063779611020055. - DOI
-
- Li J., Wang X., Zhang T., Wang C., Huang Z., Luo X., Deng Y. A review on phospholipids and their main applications in drug delivery systems. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015;10:81–98. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2014.09.004. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

