Ginsenoside Rg3 Reduces the Toxicity of Graphene Oxide Used for pH-Responsive Delivery of Doxorubicin to Liver and Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 36839713
- PMCID: PMC9965446
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020391
Ginsenoside Rg3 Reduces the Toxicity of Graphene Oxide Used for pH-Responsive Delivery of Doxorubicin to Liver and Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
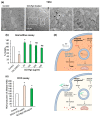
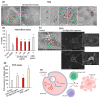
Doxorubicin (DOX) is extensively used in chemotherapy, but it has serious side effects and is inefficient against some cancers, e.g., hepatocarcinoma. To ameliorate the delivery of DOX and reduce its side effects, we designed a pH-responsive delivery system based on graphene oxide (GO) that is capable of a targeted drug release in the acidic tumor microenvironment. GO itself disrupted glutathione biosynthesis and induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation in human cells. It induced IL17-directed JAK-STAT signaling and VEGF gene expression, leading to increased cell proliferation as an unwanted effect. To counter this, GO was conjugated with the antioxidant, ginsenoside Rg3, prior to loading with DOX. The conjugation of Rg3 to GO significantly reduced the toxicity of the GO carrier by abolishing ROS production. Furthermore, treatment of cells with GO-Rg3 did not induce IL17-directed JAK-STAT signaling and VEGF gene expression-nor cell proliferation-suggesting GO-Rg3 as a promising drug carrier. The anticancer activity of GO-Rg3-DOX conjugates was investigated against Huh7 hepatocarcinoma and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. GO-Rg3-DOX conjugates significantly reduced cancer cell viability, primarily via downregulation of transcription regulatory genes and upregulation of apoptosis genes. GO-Rg3 is an effective, biocompatible, and pH responsive DOX carrier with potential to improve chemotherapy-at least against liver and breast cancers.
Keywords: doxorubicin; drug carrier; drug delivery; ginsenoside Rg3; graphene oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
Daniel van Leeuwen is currently an employee of AstraZeneca.
Figures




References
-
- Bernstein W.B. Hunter’s Tropical Medicine and Emerging Infectious Diseases. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020. Cancer in the Tropics; pp. 178–188.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

