Bioactive Polymeric Nanoparticles of Moringa oleifera Induced Phyto-Photothermal Sensitization for the Enhanced Therapy of Retinoblastoma
- PMID: 36839797
- PMCID: PMC9965703
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020475
Bioactive Polymeric Nanoparticles of Moringa oleifera Induced Phyto-Photothermal Sensitization for the Enhanced Therapy of Retinoblastoma
Abstract
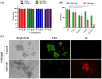
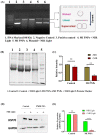
Treatment of retinoblastoma is limited due to its delayed detection and inaccesbility of drugs to reach the retina crossing the blood-retinal barrier. With the advancements in nanotechnology, photothermal therapy (PTT) employing plasmonic nanomaterials and/or NIR dyes have emerged as an affordable alternative owing to the spatial control that is offered by the modality leading to localized and enhanced therapeutic efficacy with minimal invasiveness. However, the modality is limited in its clinical application owing to the increased heat shock resistance of the tumor cells in response to the heat that is generated via PTT. Hence, in this study, we explore the role of novel biomolecular fraction of Moringa oleifera (DFM) encapsulated within a polymeric nanosystem, for its anti-heat shock protein (HSP) activity. The MO extract was co-encapsulated with NIR sensitizing dye, IR820 into a biodegradable polycaprolactone (PCL) nano-delivery system (PMIR NPs). The photothermal transduction efficacy of PMIR NPs was validated in vitro against retinoblastoma cell lines. The inherent fluorescence of DFM was utilized to evaluate the cellular internalization of the PMIR NPs using fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. The overall oxidative protein damage and downregulation of HSP70 expression upon treatment with PMIR NPs and NIR laser irradiation was evaluated using densiometric protein analysis and Western blotting. Overall, the PMIR NPs exhibited excellent anti-cancer activity when combined with PTT with downregulated HSP70 expression against retinoblastoma cells.
Keywords: Moringa oleifera; heat shock proteins; phyto-photothermal therapy; polymeric nano system; retinoblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Polydopamine encapsulated new indocyanine green theranostic nanoparticles for enhanced photothermal therapy in cervical cancer HeLa cells.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Sep 19;10:984166. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.984166. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36213060 Free PMC article.
-
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated inhibitor-loaded copper sulfide nanoparticles for low-temperature photothermal therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma.Acta Biomater. 2021 Jun;127:276-286. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.03.051. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33812073
-
A plasmon-enhanced fluorescent gold coated novel lipo-polymeric hybrid nanosystem: synthesis, characterization and application for imaging and photothermal therapy of breast cancer.Nanoscale. 2022 Jun 30;14(25):9112-9123. doi: 10.1039/d2nr01378a. Nanoscale. 2022. PMID: 35722896
-
IR820 functionalized melanin nanoplates for dual-modal imaging and photothermal tumor eradication.Nanoscale Adv. 2020 May 5;2(6):2587-2594. doi: 10.1039/d0na00236d. eCollection 2020 Jun 17. Nanoscale Adv. 2020. PMID: 36133390 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional Polymeric Nanoparticles for Chemo/Phototheranostics of Retinoblastoma.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022 Jan 10;8(1):151-160. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c01234. Epub 2021 Dec 22. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022. PMID: 34933546
Cited by
-
Light-responsive polymeric nanoparticles for retinal drug delivery: design cues, challenges and future perspectives.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 18;10(5):e26616. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26616. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38434257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in Nanosystems for Ocular Drug Delivery: A Focus on Pediatric Retinoblastoma.Molecules. 2024 May 11;29(10):2263. doi: 10.3390/molecules29102263. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38792122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review on Moringa oleifera nanoparticles: importance of polyphenols in nanoparticle synthesis, nanoparticle efficacy and their applications.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Feb 19;22(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02332-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38373982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-based delivery systems as emerging therapy in retinoblastoma: recent advances, challenges and prospects.Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Aug 15;5(18):4628-4648. doi: 10.1039/d3na00462g. eCollection 2023 Sep 12. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 37705787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polydopamine-Based Targeted Nanosystem for Chemo/Photothermal Therapy of Retinoblastoma in a Mouse Orthotopic Model.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jul 30;19:7799-7816. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S467949. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39099794 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

