Formulation Approaches to Crystalline Status Modification for Carotenoids: Impacts on Dissolution, Stability, Bioavailability, and Bioactivities
- PMID: 36839810
- PMCID: PMC9965060
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020485
Formulation Approaches to Crystalline Status Modification for Carotenoids: Impacts on Dissolution, Stability, Bioavailability, and Bioactivities
Abstract
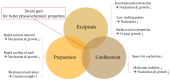
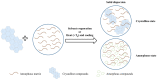
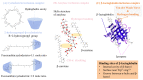
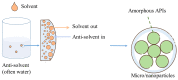
Carotenoids, including carotenes and xanthophylls, have been identified as bioactive ingredients in foods and are considered to possess health-promoting effects. From a biopharmaceutical perspective, several physicochemical characteristics, such as scanty water solubility, restricted dissolution, and susceptibility to oxidation may influence their oral bioavailability and eventually, their effectiveness. In this review, we have summarized various formulation approaches that deal with the modification of crystalline status for carotenoids, which may improve their physicochemical properties, oral absorption, and biological effects. The mechanisms involving crystalline alteration and the typical methods for examining crystalline states in the pharmaceutical field have been included, and representative formulation approaches are introduced to unriddle the mechanisms and effects more clearly.
Keywords: carotenoids; crystallization status modification; formulation approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


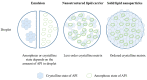
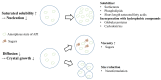

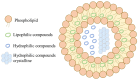
References
-
- Gary Williamson A.G.M., Graham A.B., Catherine S.B. In: Food Chemistry, Function and Analysis. Gary Williamson A.G.M., Graham A.B., Catherine S.B., editors. RSC Publishing; Cambridge, UK: 2019. pp. 15–20. - DOI
-
- Adejare A. Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2020.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

