The Effect of Super-Repressor IkB-Loaded Exosomes (Exo-srIκBs) in Chronic Post-Ischemia Pain (CPIP) Models
- PMID: 36839876
- PMCID: PMC9958867
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020553
The Effect of Super-Repressor IkB-Loaded Exosomes (Exo-srIκBs) in Chronic Post-Ischemia Pain (CPIP) Models
Abstract
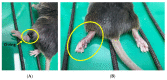
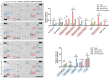
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a condition associated with neuropathic pain that causes significant impairment of daily activities and functioning. Nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) is thought to play an important role in the mechanism of CRPS. Recently, exosomes loaded with super-repressor inhibitory kappa B (Exo-srIκB, IκB; inhibitor of NFκB) have been shown to have potential anti-inflammatory effects in various inflammatory disease models. We investigated the therapeutic effect of Exo-srIκB on a rodent model with chronic post-ischemia pain (CPIP), a representative animal model of Type I CRPS. After intraperitoneal injection of a vehicle, Exo-srIκB, and pregabalin, the paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) was evaluated up to 48 h. Administration of Exo-srIκB increased PWT compared to the vehicle and pregabalin, and the relative densities of p-IκB and IκB showed significant changes compared to the vehicle 24 h after Exo-srIκB injection. The levels of several cytokines and chemokines were reduced by the administration of Exo-srIκB in mice with CPIP. In conclusion, our results showed more specifically the role of NFκB in the pathogenesis of CRPS and provided a theoretical background for novel treatment options for CRPS.
Keywords: NFκB; allodynia; chronic post-ischemic pain model; complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS); exosome loaded with super-repressor IκB; exosomes; inflammation; neuropathic pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Chulhee Choi is the founder and a shareholder of ILIAS Biologics Inc. This study is partly supported by a grant from ILIAS Biologics Inc.
Figures






References
-
- Hettne K.M., De Mos M., De Bruijn A.G., Weeber M., Boyer S., Van Mulligen E.M., Cases M., Mestres J., Van der Lei J. Applied information retrieval and multidisciplinary research: New mechanistic hypotheses in complex regional pain syndrome. J. Biomed. Discov. Collab. 2007;2:1–16. doi: 10.1186/1747-5333-2-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stanton-Hicks M. Complex regional pain syndrome. Clin. Pain Manag. A Pract. Guide. 2022;351:381–395.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

