Exosome-Based Carrier for RNA Delivery: Progress and Challenges
- PMID: 36839920
- PMCID: PMC9964211
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020598
Exosome-Based Carrier for RNA Delivery: Progress and Challenges
Abstract
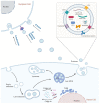
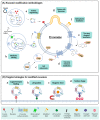
In the last few decades, RNA-based drugs have emerged as a promising candidate to specifically target and modulate disease-relevant genes to cure genetic defects. The key to applying RNA therapy in clinical trials is developing safe and effective delivery systems. Exosomes have been exploited as a promising vehicle for drug delivery due to their nanoscale size, high stability, high biocompatibility, and low immunogenicity. We reviewed and summarized the progress in the strategy and application of exosome-mediated RNA therapy. The challenges of exosomes as a carrier for RNA drug delivery are also elucidated in this article. RNA molecules can be loaded into exosomes and then delivered to targeted cells or tissues via various biochemical or physical approaches. So far, exosome-mediated RNA therapy has shown potential in the treatment of cancer, central nervous system disorders, COVID-19, and other diseases. To further exploit the potential of exosomes for RNA delivery, more efforts should be made to overcome both technological and logistic problems.
Keywords: RNA loading; RNA therapy; challenges; drug delivery; exosomes; progress; targeting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

