Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Metabolic Diversity of Wild and Cultivated Stellaria Radix (Stellaria dichotoma L. var. lanceolata Bge.)
- PMID: 36840123
- PMCID: PMC9959334
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12040775
Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Metabolic Diversity of Wild and Cultivated Stellaria Radix (Stellaria dichotoma L. var. lanceolata Bge.)
Abstract
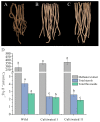
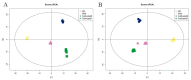
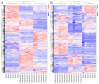
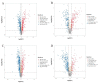
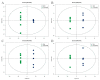
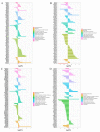
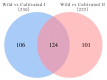
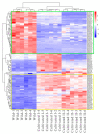
Stellaria Radix, called Yinchaihu in Chinese, is a traditional Chinese medicine, which is obtained from the dried roots of Stellaria dichotoma L. var. lanceolata Bge. Cultivated yinchaihu (YCH) has become a main source of production to alleviate the shortage of wild plant resources, but it is not clear whether the metabolites of YCH change with the mode of production. In this study, the contents of methanol extracts, total sterols and total flavonoids in wild and cultivated YCH are compared. The metabolites were analyzed by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The content of methanol extracts of the wild and cultivated YCH all exceeded the standard content of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. However, the contents of total sterols and total flavonoids in the wild YCH were significantly higher than those in the cultivated YCH. In total, 1586 metabolites were identified by mass spectrometry, and 97 were significantly different between the wild and cultivated sources, including β-sitosterol, quercetin derivatives as well as many newly discovered potential active components, such as trigonelline, arctiin and loganic acid. The results confirm that there is a rich diversity of metabolites in the wild and cultivated YCH, and provide a useful theoretical guidance for the evaluation of quality in the production of YCH.
Keywords: Stellaria dichotoma L. var. lanceolata Bge.; cultivation; medicinal plants; metabolic diversity; metabolomic; wild.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative metabolomics provides novel insights into correlation between dominant habitat factors and constituents of Stellaria Radix (Stellaria dichotoma L. var. lanceolata Bge.).Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 25;13:1035712. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1035712. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36507406 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Growth Years on the Medicinal Material Characteristics and Metabolites of Stellaria dichotoma L. var. lanceolata Bge. Reveals the Optimal Harvest Age.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jun 12;12(12):2286. doi: 10.3390/plants12122286. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375910 Free PMC article.
-
[Studies on identification of yinchaihu by UV and IR].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 1999 Aug;24(8):454-6, 509. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 1999. PMID: 12205861 Chinese.
-
[Studies on the constituents in the water extracts in crude drugs. IV. On the roots of Stellaria dichotoma L. var lanceolata Bge. (2(2)) (author's transl)].Yakugaku Zasshi. 1982 Mar;102(3):292-4. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.102.3_292. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1982. PMID: 7108760 Japanese. No abstract available.
-
[Ecological protection of medicinal woody plants].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2003 Sep;14(9):1561-4. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2003. PMID: 14733021 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive model for predicting the development of defense system of Capparis spinosa L.: a novel approach to assess the physiological indices.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 31;13(1):12413. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39683-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37524793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Z., Song L., Lei Y., Liang W., Wang H., Peng L. Advances in Biology, Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Stellaria Dichotoma var.Lanceolata. J. Nanjing Univ. Chin. Med. 2020;36:136–140. doi: 10.14148/j.issn.1672-0482.2020.0136. - DOI
-
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee . Chinese Pharmacopoeia. China Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press; Beijing, China: 2020. p. 317. 2020 ed.
-
- Mudge E., Applequist W.L., Finley J., Lister P., Townesmith A.K., Walker K.M., Brown P.N. Variation of select flavonols and chlorogenic acid content of elderberry collected throughout the Eastern United States. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016;47:52–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2015.12.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Z., Cui Y., Qin X. Challenge of quality evaluation of traditional Chinese medicinal materials and application progress on metabolomic approach in its quality valuation. Chin. Herb. Med. 2018;49:2221–2229. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.10.001. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

