Genetically engineered cellular nanoparticles for biomedical applications
- PMID: 36841215
- PMCID: PMC10542936
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122065
Genetically engineered cellular nanoparticles for biomedical applications
Abstract
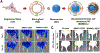
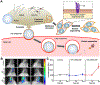
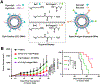
In recent years, nanoparticles derived from cellular membranes have been increasingly explored for the prevention and treatment of human disease. With their flexible design and ability to interface effectively with the surrounding environment, these biomimetic nanoparticles can outperform their traditional synthetic counterparts. As their popularity has increased, researchers have developed novel ways to modify the nanoparticle surface to introduce new or enhanced capabilities. Moving beyond naturally occurring materials derived from wild-type cells, genetic manipulation has proven to be a robust and flexible method by which nanoformulations with augmented functionalities can be generated. In this review, an overview of genetic engineering approaches to express novel surface proteins is provided, followed by a discussion on the various biomedical applications of genetically modified cellular nanoparticles.
Keywords: Biomimetic nanoparticle; Cell membrane coating; Detoxification; Drug delivery; Genetic engineering; Immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Liangfang Zhang reports financial support was provided by Defense Threat Reduction Agency. Ronnie Fang reports financial support was provided by National Institutes of Health.
Figures

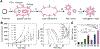
Similar articles
-
Coating nanoparticles with cell membranes for targeted drug delivery.J Drug Target. 2015;23(7-8):619-26. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2015.1052074. J Drug Target. 2015. PMID: 26453159 Review.
-
Cell Membrane-Cloaked Nanotherapeutics for Targeted Drug Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 17;23(4):2223. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042223. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Membrane Coating Nanotechnology.Adv Mater. 2018 Jun;30(23):e1706759. doi: 10.1002/adma.201706759. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Adv Mater. 2018. PMID: 29582476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles for drug delivery.J Control Release. 2015 Dec 28;220(Pt B):600-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.07.019. Epub 2015 Jul 23. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 26210440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered Cell Membrane Coating Technologies for Biomedical Applications: From Nanoscale to Macroscale.ACS Nano. 2025 Apr 1;19(12):11517-11546. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c16280. Epub 2025 Mar 24. ACS Nano. 2025. PMID: 40126356 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineered Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Feb 23;14(5):413. doi: 10.3390/nano14050413. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38470744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver cirrhosis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions.MedComm (2020). 2024 Sep 17;5(10):e721. doi: 10.1002/mco2.721. eCollection 2024 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39290252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioengineered nanotechnology for nucleic acid delivery.J Control Release. 2023 Dec;364:124-141. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.10.034. Epub 2023 Oct 27. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 37879440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhalable hybrid nanovaccines with virus-biomimetic structure boost protective immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 variants.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Feb 27;22(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02345-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38414031 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle approaches for manipulating cytokine delivery and neutralization.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 10;16:1592795. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1592795. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40557148 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Farokhzad OC, Langer R, Impact of nanotechnology on drug delivery, ACS Nano 3 (1) (2009) 16–20. - PubMed
-
- Farokhzad OC, Langer R, Nanomedicine: Developing smarter therapeutic and diagnostic modalities, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 58 (14) (2006) 1456–1459. - PubMed
-
- Wang AZ, Langer R, Farokhzad OC, Nanoparticle delivery of cancer drugs, Annu. Rev. Med 63 (2012) 185–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

