Hidden behavioral fingerprints in epilepsy
- PMID: 36841241
- PMCID: PMC10164063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.02.003
Hidden behavioral fingerprints in epilepsy
Abstract
Epilepsy is a major disorder affecting millions of people. Although modern electrophysiological and imaging approaches provide high-resolution access to the multi-scale brain circuit malfunctions in epilepsy, our understanding of how behavior changes with epilepsy has remained rudimentary. As a result, screening for new therapies for children and adults with devastating epilepsies still relies on the inherently subjective, semi-quantitative assessment of a handful of pre-selected behavioral signs of epilepsy in animal models. Here, we use machine learning-assisted 3D video analysis to reveal hidden behavioral phenotypes in mice with acquired and genetic epilepsies and track their alterations during post-insult epileptogenesis and in response to anti-epileptic drugs. These results show the persistent reconfiguration of behavioral fingerprints in epilepsy and indicate that they can be employed for rapid, automated anti-epileptic drug testing at scale.
Keywords: 3D video; behavior; biomarkers; drug screening; epilepsy; machine learning; phenotyping.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
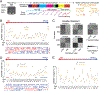
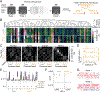
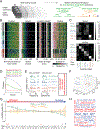
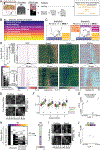
Comment in
-
AI-nalyzing Mouse Behavior to Combat Epilepsy.Epilepsy Curr. 2023 Jul 7;23(5):315-317. doi: 10.1177/15357597231185215. eCollection 2023 Sep-Oct. Epilepsy Curr. 2023. PMID: 37901783 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

