Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 36841646
- PMCID: PMC9884619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.medcli.2023.01.012
Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
Objectives: The aim was to compare the incidence of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 adult patients during the pandemic period versus the previous two years. Also, we described the characteristics of both cohorts of patients in pandemic period to find differences.
Material and methods: Retrospective study in our tertiary-care centre reviewing S. aureus bacteremia episodes in COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients through clinical records and the Microbiology Department database.
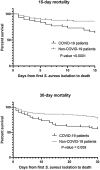
Results: In 2018 and 2019, the incidence of S. aureus bacteremia episodes was 1.95 and 1.63 per 1000 admissions respectively. In the pandemic period, global incidence was 1.96 episodes per 1000 non-COVID-19 admissions and 10.59 episodes per 1000 COVID-19 admissions. A total of 241 bacteremia was registered during this pandemic period in 74 COVID-19 patients and in 167 non-COVID-19 patients. Methicillin resistance was detected in 32.4% and 13.8% of isolates from COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients respectively. In COVID-19 patients, mortality rates were significantly higher.
Conclusions: We showed a significantly high rates of S. aureus bacteremia incidence in COVID-19 patients and higher methicillin resistance and 15-day mortality rates than in non-COVID-19 patients.
Objetivos: Comparar la incidencia de bacteriemias por Staphylococcus aureus en pacientes adultos COVID-19 y no-COVID-19 durante la pandemia frente a los 2 años previos. Además, describimos las características de ambas cohortes en periodo pandémico para encontrar diferencias.
Material y métodos: Estudio retrospectivo en nuestro centro de tercer nivel a través de historias clínicas y la base de datos del Servicio de Microbiología.
Resultados: En 2018 y 2019, la incidencia de bacteriemias fue de 1.95 y 1,63 casos por cada 1.000 ingresos respectivamente. En pandemia, la incidencia global fue de 1,96 casos por cada 1.000 ingresos no-COVID-19 y de 10,59 casos por cada 1.000 ingresos COVID-19. Durante la pandemia se registraron 241 bacteriemias en 74 pacientes COVID-19 y en 167 pacientes no-COVID-19. La resistencia a meticilina se detectó en el 32,4 y 13,8% de los aislados de pacientes COVID-19 y no-COVID-19 respectivamente. En pacientes COVID-19 la mortalidad fue significativamente mayor.
Conclusiones: Mostramos una incidencia significativamente alta de bacteriemias por S. aureus en pacientes COVID-19, así como mayores tasas de resistencia a meticilina y mortalidad a los 15 días que en pacientes no-COVID-19.
Keywords: Bacteremia; Bacteriemia; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Staphylococcus aureus.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous