Removal of toxic lead from aqueous solution using a low-cost adsorbent
- PMID: 36841837
- PMCID: PMC9968331
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-29674-x
Removal of toxic lead from aqueous solution using a low-cost adsorbent
Abstract
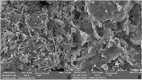
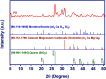
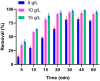
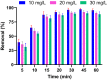
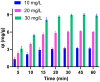
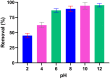
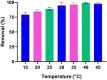
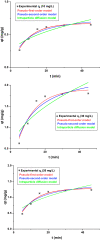
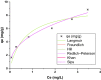
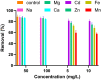
Valorization of waste materials and byproducts as adsorbents is a sustainable approach for water treatment systems. Pottery Granules (PG) without any chemical and thermal modification were used as a low-cost, abundant, and environmentally benign adsorbent against Pb(II), the toxic metal in drinking water. The porous structure and complex mineral composition of PG made it an efficient adsorbent material for Pb(II). The effect of key physicochemical factors was investigated to determine the significance of contact time, PG dose, pH, solution temperature, and coexisting ions, on the process. Pb(II) removal increased by PG dose in the range of 5-15 g/L, and agitation time from 5 to 60 min. Increasing Pb(II) concentration led to a drop in Pb(II) removal, however, adsorption capacity increased significantly as concentration elevated. Pb(II) removal also increased significantly from ~ 45% to ~ 97% by pH from 2 to 12. A ~ 20% improvement in Pb(II) adsorption after rising the solution temperature by 30˚C, indicated the endothermic nature of the process. The sorption was described to be a favorable process in which Pb(II) was adsorbed in a multilayer onto the heterogeneous PG surface. The qmax of 9.47 mg/g obtained by the Langmuir model was superior among many reported low-cost adsorbents. The Pb(II) adsorption was described well by the Pseudo- first-order kinetic model. Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+ showed a negligible effect on Pb(II) adsorption. However, the presence of Mn2+ and Fe2+ significantly hindered the process efficacy. In conclusion, the use of waste material such as PG against Pb(II) is a viable option from the economic and effectiveness points of view.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimization and mechanisms of methylene blue removal by foxtail millet shell from aqueous water and reuse in biosorption of Pb(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) for secondary times.Int J Phytoremediation. 2022;24(4):350-363. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2021.1944978. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Int J Phytoremediation. 2022. PMID: 34410866
-
Adsorption of Pb(II) ions from contaminated water by 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic acid-modified microcrystalline cellulose: Isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Dec 1;164:3193-3203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.159. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32853617
-
Carnauba (Copernicia prunifera) palm tree biomass as adsorbent for Pb(II) and Cd(II) from water medium.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Apr;28(15):18941-18952. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-07635-5. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 31933097
-
Chitosan grafted tetracarboxylic functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for removal of Pb(II) from an aqueous environment.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jan 15;225:1517-1528. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.11.208. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36427619
-
Natural, low-cost adsorbents for toxic Pb(II) ion sequestration from (waste)water: A state-of-the-art review.Chemosphere. 2022 Jan;287(Pt 2):132130. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132130. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34517237 Review.
Cited by
-
Parametric study and process modeling for metronidazole removal by rhombic dodecahedron ZIF-67 crystals.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 5;13(1):14654. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41724-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37669982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sani A, Idris KM, Abdullahi BA, Darma AI. Bioaccumulation and health risks of some heavy metals in Oreochromis niloticus, sediment and water of Challawa river, Kano, Northwestern Nigeria. Environ. Adv. 2022;7:100172. doi: 10.1016/j.envadv.2022.100172. - DOI
-
- Narasimharao K, et al. Synthesis and characterization of hexagonal MgFe layered double hydroxide/grapheme oxide nanocomposite for efficient adsorptive removal of cadmium ion from aqueous solutions: Isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanism. J. Water Process Eng. 2022;47:102746. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102746. - DOI
-
- El-Arish N, Zaki RM, Miskan S, Setiabudi H, Jaafar N. Adsorption of Pb (II) from aqueous solution using alkaline-treated natural zeolite: Process optimization analysis. Total Environ. Res. Themes. 2022;3:100015. doi: 10.1016/j.totert.2022.100015. - DOI
-
- Dehghani, M. & Fadaei, A. Potoccatalytic oxidation of oganophosphorus pesticides using zinc oxide. Res. J. Chem. Environ.16. 10.1039/D0RA01741H (2012).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

