Long non-coding RNA-derived peptides are immunogenic and drive a potent anti-tumour response
- PMID: 36841868
- PMCID: PMC9968330
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36826-0
Long non-coding RNA-derived peptides are immunogenic and drive a potent anti-tumour response
Abstract
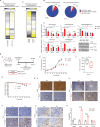
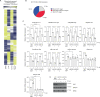
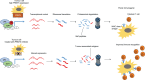
Protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) 5 is over-expressed in a variety of cancers and the master transcription regulator E2F1 is an important methylation target. We have explored the role of PRMT5 and E2F1 in regulating the non-coding genome and report here a striking effect on long non-coding (lnc) RNA gene expression. Moreover, many MHC class I protein-associated peptides were derived from small open reading frames in the lncRNA genes. Pharmacological inhibition of PRMT5 or adjusting E2F1 levels qualitatively altered the repertoire of lncRNA-derived peptide antigens displayed by tumour cells. When presented to the immune system as either ex vivo-loaded dendritic cells or expressed from a viral vector, lncRNA-derived peptides drove a potent antigen-specific CD8 T lymphocyte response, which translated into a significant delay in tumour growth. Thus, lncRNA genes encode immunogenic peptides that can be deployed as a cancer vaccine.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Immunogenic Lncs to cancer therapy.Sci Signal. 2023 Mar 7;16(775):eadh4085. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.adh4085. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Sci Signal. 2023. PMID: 36881653
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

