Development and validation of a liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric assay for the quantification of cabotegravir and rilpivirine from dried blood spots
- PMID: 36842333
- PMCID: PMC10065945
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115307
Development and validation of a liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric assay for the quantification of cabotegravir and rilpivirine from dried blood spots
Abstract
Background: Dried blood spots (DBS) have been utilized as a blood plasma alternative for therapeutic drug monitoring and pharmacologic analysis. There are analytical and physiochemical considerations in bridging drug concentrations from plasma to DBS. Recently, the long-acting antiretroviral cabotegravir (CAB) has been approved for HIV prevention, and a co-packaged regimen of long-acting CAB and rilpivirine (RPV) has been approved for HIV treatment. Measurement of these drugs in blood collected as DBS may offer increased capacity and flexibility in translational applications.
Methods: Whole blood was spiked with CAB and RPV and spotted on DBS cards. Following extraction and addition of isotopically labeled internal standards, samples were subjected to liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric (LC-MS/MS) analysis. The method was validated according to regulatory recommendations, and the assay was evaluated in remnant samples from an HIV prevention trial in which paired DBS and plasma samples were collected.
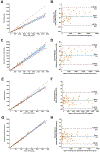
Results: DBS CAB and RPV concentrations were linear from 25 to 20,000 ng/mL and 2-2500 ng/mL, respectively. Precision, accuracy, and matrix effect results were acceptable. DBS RPV demonstrated stability under all tested conditions; DBS CAB showed mean biases of - 23.5% when stored at room temperature for 36 days, and - 18.0% at 40 °C and 100% humidity for two days. DBS measurements for CAB and RPV were an average 54.0% and 14.1% lower, respectively, as compared to paired plasma samples. Derived conversion factors of 1.79 and 1.16 were applied to DBS CAB and RPV measurements, respectively, to estimate plasma concentrations. Estimated plasma CAB and RPV concentrations showed mean biases of 2.2% and 0.6%, respectively. In a CAB clinical trial, application of the conversion factor resulted in agreement between estimated plasma CAB concentrations from DBS and plasma CAB concentrations (y = 1.08x - 79.2, r = 0.932; mean bias of -3.2%; 95% CI: -48.2% to 41.9%).
Conclusions: We developed and validated a novel LC-MS/MS assay for the quantification of CAB and RPV from DBS, and identified conversion factors to estimate plasma concentrations from spotted blood.
Keywords: Cabotegravir; DBS; HIV; LC-MS; Mass spectrometry; Rilpivirine.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
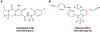

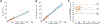
References
-
- UNAIDS, IN DANGER: UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2022. Geneva: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/ AIDS; 2022. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO., 2022.
-
- United Stated Food and Drug Administration, FDA Approves Cabenuva and Vocabria for the Treatment of HIV-1 Infection, (2021). https://www.fda.gov/drugs/human-immunodeficiency-virus-hiv/fda-approves-... (accessed November 29, 2022).
-
- United Stated Food and Drug Administration, FDA Approves First Injectable Treatment for HIV Pre-Exposure Prevention, (2021). https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-i... (accessed November 29, 2022).
-
- UNAIDS welcomes the approval of long-acting injectable cabotegravir as a pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention, (n.d.). https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/presscentre/pressreleaseandstatement... (accessed December 1, 2022).
-
- Johns BA, Kawasuji T, Weatherhead JG, Taishi T, Temelkoff DP, Yoshida H, Akiyama T, Taoda Y, Murai H, Kiyama R, Fuji M, Tanimoto N, Jeffrey J, Foster SA, Yoshinaga T, Seki T, Kobayashi M, Sato A, Johnson MN, Garvey EP, Fujiwara T, Carbamoyl pyridone HIV-1 integrase inhibitors 3. A diastereomeric approach to chiral nonracemic tricyclic ring systems and the discovery of dolutegravir (S/GSK1349572) and (S/GSK1265744), J Med Chem. 56 (2013) 5901–5916. 10.1021/jm400645w. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

