Prospecting of exosomal-miRNA signatures as prognostic marker for gestational diabetes mellitus and other adverse pregnancy outcomes
- PMID: 36843574
- PMCID: PMC9946972
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1097337
Prospecting of exosomal-miRNA signatures as prognostic marker for gestational diabetes mellitus and other adverse pregnancy outcomes
Abstract
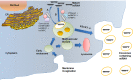
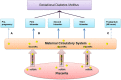
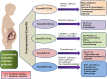
Exosomal microRNA (ExomiRs) serves as potential cargo molecules responsible for post-translation of gene expression and intracellular communication playing a vital role in acting as clinically relevant prognostic biomarkers for identifying pregnancy-associated complications in patients. ExomiRs are associated with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) as potential targets for understanding the pathophysiology of beta-cell dysfunction. ExomiRs (ExomiR 122, ExomiR 16-5p, ExomiR 215-5p, ExomiR 450b-3p, ExomiR 122-5p) aid to act as biomarkers and regulate the progression of diabetes and its related complication. These ExomiRshave been reported to interfere with the regulation of various genes such as ZEB2, IRS1, IRS2, GLUT1, GLUT4, etc. and inhibition of several pathways like PI3K/AKT, Wnt, and mTOR signaling pathways leading to the modulation in the development of GDM affecting the clinical and pathological features of women. These ExomiRs have also been associated with other pregnancy-associated complications, including preeclampsia, hypothyroidism, pregnancy loss, and ectopic pregnancies. On the other hand, overexpression of certain ExomiRs such as Exomir-515-5p, ExomiR-221, and ExomiR-96 serve a regulatory role in overcoming insulin resistance. Taken together, the current review focuses on the prospective capabilities of ExomiRs for diagnosis and clinical prognosis of GDM women with respect to pregnancy outcomes.
Keywords: clinical prognosis; exosomal microRNA; gestational diabetes mellitus; pregnancy outcomes; signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2023 Mitra, Gulati, Uppal, Kumari, Tripathy, Ranjan and Janardhanan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

