UFL1, a UFMylation E3 ligase, plays a crucial role in multiple cellular stress responses
- PMID: 36843575
- PMCID: PMC9950256
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1123124
UFL1, a UFMylation E3 ligase, plays a crucial role in multiple cellular stress responses
Abstract
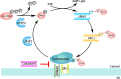
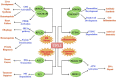
The UFM1 conjugation system(UFMylation)is a novel type of ubiquitin-like system that plays an indispensable role in maintaining cell homeostasis under various cellular stress. Similar to ubiquitination, UFMylation consists of a three-step enzymatic reaction with E1-like enzymes ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme5 (UBA5), E2-like enzymes ubiquitin-fold modifier-conjugating enzyme 1(UFC1), and E3-like ligase UFM1-specific ligase 1 (UFL1). As the only identified E3 ligase, UFL1 is responsible for specific binding and modification of the substrates to mediate numerous hormone signaling pathways and endocrine regulation under different physiological or pathological stress, such as ER stress, genotoxic stress, oncogenic stress, and inflammation. Further elucidation of the UFL1 working mechanism in multiple cellular stress responses is essential for revealing the disease pathogenesis and providing novel potential therapeutic targets. In this short review, we summarize the recent advances in novel UFL1 functions and shed light on the potential challenges ahead, thus hopefully providing a better understanding of UFMylation-mediated cellular stress.
Keywords: ER stress; UFL1; Ufmylation modification; genotoxic stress; inflammation; oncogenic stress.
Copyright © 2023 Jiang, Wang, Xiang, Hua, Zhou, Chen, Lv, Huang and Cai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ufl1/RCAD, a Ufm1 E3 ligase, has an intricate connection with ER stress.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Aug 15;135:760-767. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.170. Epub 2019 May 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 31129212 Review.
-
UFMylation: A Unique & Fashionable Modification for Life.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun;14(3):140-146. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 May 20. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27212118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel type of E3 ligase for the Ufm1 conjugation system.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 19;285(8):5417-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.036814. Epub 2009 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20018847 Free PMC article.
-
UFMylation System: An Emerging Player in Tumorigenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 19;14(14):3501. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143501. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deficiency of Murine UFM1-Specific E3 Ligase Causes Microcephaly and Inflammation.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Oct;59(10):6363-6372. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02979-0. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35931931
Cited by
-
Role of UFMylation in tumorigenesis and cancer immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 23;15:1454823. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1454823. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39247188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UFMylation: A supervisor of the HIF1α pathway and a potential therapeutic target for anti-PD-1 combination therapy in hypoxic tumors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jul 8;122(27):e2500562122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2500562122. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40601633 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping adipocyte interactome networks by HaloTag-enrichment-mass spectrometry.Biol Methods Protoc. 2024 May 29;9(1):bpae039. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpae039. eCollection 2024. Biol Methods Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38884001 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on the functional role of UFMylation in cells (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jul;32(1):191. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13556. Epub 2025 May 9. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40341950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A statistical mechanics investigation of unfolded protein response across organisms.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 12;14(1):27658. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79086-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39532983 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials