Zinc restores functionality in porcine prepubertal Sertoli cells exposed to subtoxic cadmium concentration via regulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway
- PMID: 36843583
- PMCID: PMC9950629
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.962519
Zinc restores functionality in porcine prepubertal Sertoli cells exposed to subtoxic cadmium concentration via regulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway
Abstract
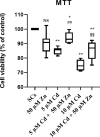
Introduction: Among substances released into the environment by anthropogenic activities, the heavy metal cadmium (Cd) is known to induce severe testicular injury causing male subfertility/infertility. Zinc (Zn) is another heavy metal that, unlike Cd, is physiologically present in the testis, being essential for spermatogenesis. We aimed to examine the possibility that 50 µM ZnCl2 could counteract the toxic effects induced by Cd in an in vitro model of porcine prepubertal Sertoli cells (SCs) exposed to both subtoxic (5 μM) and toxic (10 μM) concentrations of CdCl2 for 48 h.
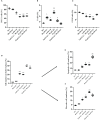
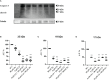
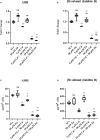
Materials and methods: Apoptosis, cell cycle, and cell functionality were assessed. The gene expression of Nrf2 and its downstream antioxidant enzymes, ERK1/2, and AKT kinase signaling pathways were evaluated.
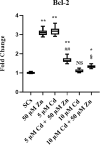
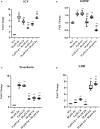
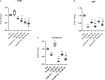
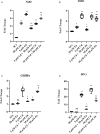
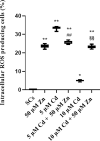
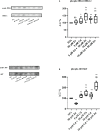
Materials and results: We found that Zn, in co-treatment with subtoxic and toxic Cd concentration, increased the number of metabolically active SCs compared to Cd exposure alone but restored SC functionality only in co-treatment with subtoxic Cd concentration with respect to subtoxic Cd alone. Exposure of Cd disrupted cell cycle in SCs, and Zn co-treatment was not able to counteract this effect. Cd alone induced SC death through apoptosis and necrosis in a dose-dependent manner, and co-treatment with Zn increased the pro-apoptotic effect of Cd. Subtoxic and toxic Cd exposures activated the Nrf2 signaling pathway by increasing gene expression of Nrf2 and its downstream genes (SOD, HO-1, and GSHPx). Zn co-treatment with subtoxic Cd attenuated upregulation on the Nrf2 system, while with toxic Cd, the effect was more erratic. Studying ERK1/2 and AKT pathways as a target, we found that the phosphorylation ratio of p-ERK1/2 and p-AKT was upregulated by both subtoxic and toxic Cd exposure alone and in co-treatment with Zn.
Discussion: Our results suggest that Zn could counteract Cd effects by increasing the number of metabolically active SCs, fully or partially restoring their functionality by modulating Nrf2, ERK1/2, and AKT pathways. Our SC model could be useful to study the effects of early Cd exposure on immature testis, evaluating the possible protective effects of Zn.
Keywords: Nrf2 signaling pathway; Sertoli cells; cadmium; oxidative stress; zinc.
Copyright © 2023 Mancuso, Arato, Bellucci, Lilli, Eugeni, Aglietti, Stabile, Pistilli, Brancorsini, Gaggia, Calvitti, Baroni and Luca.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

