Prognostic value of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in IgA nephropathy and establishment of nomogram model
- PMID: 36843611
- PMCID: PMC9950098
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1037773
Prognostic value of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in IgA nephropathy and establishment of nomogram model
Abstract
Background: Dyslipidemia is closely related to kidney disease. We aimed to investigate the relationship between low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and prognosis of IgA nephropathy (IgAN) and build a nomogram prognostic model.
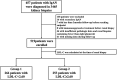
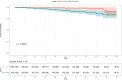
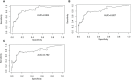
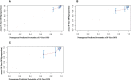
Methods: 519 IgAN patients with 61 months median follow-up were enrolled and divided into two groups based on the cut-off value of baseline LDL-C (2.60 mmol/L): the high group (n=253) and the low group (n=266). Renal survival was assessed by Kaplan⁃Meier (KM) survival curve. Risk factors were identified by COX regression analysis. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (AUC), concordance index (C-index), and calibration curves were applied to evaluate the nomogram model.
Results: KM survival curve analysis showed that the high LDL-C group had worse renal survival than the low LDL-C group (χ2 = 8.555, p=0.003). After adjusting for confounding factors, Cox regression analysis showed the baseline LDL-C level was an independent risk factor of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in IgAN (HR=3.135, 95% CI 1.240~7.926, p =0.016). LDL-C, segmental sclerosis, tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis, the prevalence of cardiovascular disease, 24-hour proteinuria were identified and entered into the nomogram models, with AUC of 0.864, 0.827, and 0.792 respectively to predict the 5-, 8-, and 10-year risk of ESRD in IgAN. The C-index of this prediction model was respectively 0.862, 0.838, and 0.800 and was well-calibrated.
Conclusion: Elevated LDL-C level is a predictive factor for the prognosis of IgAN. We developed a nomogram model that can predict the risk of ESRD in IgAN by using LDL-C ≥ 2.60 mmol/L.
Keywords: ESRD; IgA nephropathy; low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; nomogram prognostic model; prognosis.
Copyright © 2023 Tian, Li, Chu, Hu, Xie and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Piepoli MF, Hoes AW, Agewall S, Albus C, Brotons C, Catapano AL, et al. . 2016 European guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The sixth joint task force of the European society of cardiology and other societies on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts)Developed with the special contribution of the European association for cardiovascular prevention & rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur Heart J (2016) 37(29):2315–81. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

