False-Positive Human Immunodeficiency Virus Results in COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 36843732
- PMCID: PMC9946275
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.34096
False-Positive Human Immunodeficiency Virus Results in COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus, which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) disease, was first described in 2019 and became a pandemic in 2020. Although it is possible for two viruses to co-infect together, a rarer phenomenon of false-positive results due to cross-reactivity between viruses is also possible. Herein, we present two cases of the false-positive human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) results in those infected with COVID-19. Both patients were screened for HIV and were initially found to be positive with the fourth-generation test. A subsequent blood test revealed no viral load, and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) test indicated no reactivity to HIV, thus the false initial screening test. SARS-CoV-2 is an enveloped RNA virus with its outer surface containing a spike-like glycoprotein, which allows it to recognize host cells and invade. HIV-1 gp41 and SARS-CoV-2 share several structural sequences and motifs. These similarities could explain cross-reactivity and false-positive results when screening for HIV in the presence of COVID. The presence of HIV must be confirmed through more specific laboratory tests such as ELISA.
Keywords: covid-19; enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (elisa); fourth generation hiv screening test; human immunodeficiency virus infection; sars-cov-2.
Copyright © 2023, Hakobyan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
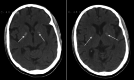
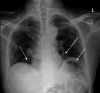
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
