Pediatric Patients With Hemiplegia: A Systematic Review of a Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36843815
- PMCID: PMC9946895
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.34074
Pediatric Patients With Hemiplegia: A Systematic Review of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
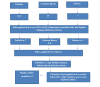
Hemiplegia is the medical term for paralysis of one side of the body. It results in muscular wasting on the affected side, impairs gait, reduces motor abilities, and causes instability and a loss of grasping capacity. The patient's quality of life is impacted by hemiplegia because it impairs brain and spinal cord functions. Consequently, a range of therapeutic options, including physical therapy, medical health management, and other multidisciplinary care, are accessible. The effects of treatments on juvenile patients with hemiplegia who are participating in a randomized controlled trial (RCT) are examined in this systematic review. Using the Boolean operator "AND," the research process entailed searching for keywords like "Hemiplegia" and "Pediatrics." Based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, a total of six RCTs were included in the study. According to the study's findings, hemiplegic patients benefited from Kinesio taping (KT), botulinum toxin type-A (BoNT-A), hyaluronic acid injections, and bimanual treatment.
Keywords: hemiplegia; kinesio taping; pediatric; randomized controlled trial; systematic review.
Copyright © 2023, Varma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Hemiplegia. [ Oct; 2022 ];Raman TS, Surendran KK, Gupta RK, Gupta AK, Ravichander Ravichander, Sood SL. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9251281/ Indian Pediatr. 1997 34:55–59. - PubMed
-
- Effect of kinesiology taping on hemiplegic shoulder pain and functional outcomes in subacute stroke patients: a randomized controlled study. Huang YC, Leong CP, Wang L, et al. https://europepmc.org/article/med/27575012. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;52:774–781. - PubMed
-
- Injection frequency of botulinum toxin A for spastic equinus: a randomized clinical trial. Hastings-Ison T, Blackburn C, Rawicki B, Fahey M, Simpson P, Baker R, Graham K. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2016;58:750–757. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources