How to use COVID-19 antiviral drugs in patients with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 36843922
- PMCID: PMC9947246
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1053814
How to use COVID-19 antiviral drugs in patients with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
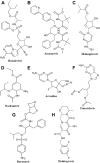
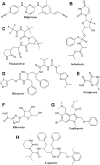
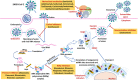
Antiviral drugs such as Remdesivir (Veklury), Nirmatrelvir with Ritonavir (Paxlovid), Azvudine, and Molnupiravir (Lagevrio) can reduce the risk for severe and fatal Coronavirus Disease (COVID)-19. Although chronic kidney disease is a highly prevalent risk factor for severe and fatal COVID-19, most clinical trials with these drugs excluded patients with impaired kidney function. Advanced CKD is associated with a state of secondary immunodeficiency (SIDKD), which increases the susceptibility to severe COVID-19, COVID-19 complications, and the risk of hospitalization and mortality among COVID-19 patients. The risk to develop COVID-19 related acute kidney injury is higher in patients with precedent CKD. Selecting appropriate therapies for COVID-19 patients with impaired kidney function is a challenge for healthcare professionals. Here, we discuss the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of COVID-19-related antiviral drugs with a focus on their potential use and dosing in COVID-19 patients with different stages of CKD. Additionally, we describe the adverse effects and precautions to be taken into account when using these antivirals in COVID-19 patients with CKD. Lastly, we also discuss about the use of monoclonal antibodies in COVID-19 patients with kidney disease and related complications.
Keywords: COVID-19; antivirals; chronic kidney disease; clinical trials; monoclonal antibodies; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics.
Copyright © 2023 Kale, Shelke, Dagar, Anders and Gaikwad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdalla S., Elgassim L., Rustom F., Othman M. (2020). Acute kidney injury caused by darunavir in a patient with COVID-19: A case report. Open J. Nephrol. 10 (4), 375–382. 10.4236/ojneph.2020.104037 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

