Insights of Chinese herbal medicine for mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced cognitive impairment: Existed evidences and potential directions
- PMID: 36843941
- PMCID: PMC9950122
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1138566
Insights of Chinese herbal medicine for mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced cognitive impairment: Existed evidences and potential directions
Abstract
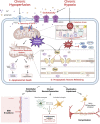
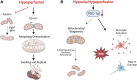
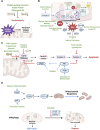
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH) is one of the main pathophysiological markers of cognitive impairment in central nervous system diseases. Mitochondria are cores of energy generation and information process. Mitochondrial dysfunction is the key upstream factors of CCH induced neurovascular pathology. Increasing studies explored the molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial dysfunction and self-repair for effective targets to improve CCH-related cognitive impairment. The clinical efficacy of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of CCH induced cognitive impairment is definite. Existed evidences from pharmacological studies have further proved that, Chinese herbal medicine could improve mitochondrial dysfunction and neurovascular pathology after CCH by preventing calcium overload, reducing oxidative stress damage, enhancing antioxidant capacity, inhibiting mitochondria-related apoptosis pathway, promoting mitochondrial biogenesis and preventing excessive activation of mitophagy. Besides, CCH mediated mitochondrial dysfunction is one of the fundamental causes for neurodegeneration pathology aggravation. Chinese herbal medicine also has great potential therapeutic value in combating neurodegenerative diseases by targeting mitochondrial dysfunction.
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine; chronic cerebral hypoperfusion; cognitive impairment; mitochondria; mitochondrial dysfunction.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Wang, Li, Jin, Duan, Lu, Qin, Song, Li and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dimethyl fumarate improves cognitive deficits in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats by alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis via NRF2/ARE/NF-κB signal pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Sep;98:107844. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107844. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34153667
-
Low-intensity treadmill exercise protects cognitive impairment by enhancing cerebellar mitochondrial calcium retention capacity in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.J Exerc Rehabil. 2021 Oct 26;17(5):324-330. doi: 10.12965/jer.2142544.272. eCollection 2021 Oct. J Exerc Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 34805021 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering mitochondrial dysfunction: Pathophysiological mechanisms in vascular cognitive impairment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 May;174:116428. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116428. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38599056 Review.
-
Xi-Xian-Tong-Shuan capsule alleviates vascular cognitive impairment in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats by promoting white matter repair, reducing neuronal loss, and inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory factors.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Jan;145:112453. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112453. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 34808554
-
From chronic cerebral hypoperfusion to Alzheimer-like brain pathology and neurodegeneration.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Jan;35(1):101-10. doi: 10.1007/s10571-014-0127-9. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25352419 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Necroptosis in vascular cognitive impairment: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Jun 25;17:1599773. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1599773. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40636901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALDH2 Overexpression Improves the Blood-brain Barrier and Represses Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion Through the SIRT1/ROS Axis.Neurochem Res. 2025 Feb 18;50(2):102. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04353-7. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 39964551
-
Research progress of mitophagy in chronic cerebral ischemia.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Aug 3;15:1224633. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1224633. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37600521 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bai X., Tang H. M., Ye L. S., Yang Y. F., Zhang D. C., Luo G. (2014). Effects of Qufeng Tongqiao Formula on hippocampal mitochondrial cox activity and Coxⅱmrna expression in vascular dementia rats. Jiangsu J. Trad. Chin. Med. 46, 75–77.
-
- Calegari V. C., Zoppi C. C., Rezende L. F., Silveira L. R., Carneiro E. M., Boschero A. C. (2011). Endurance training activates amp-activated protein kinase, increases expression of uncoupling protein 2 and reduces insulin secretion from rat pancreatic islets. J. Endocrinol. 208, 257–264. 10.1530/joe-10-0450 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

