Roxadustat, a HIF-PHD inhibitor with exploitable potential on diabetes-related complications
- PMID: 36843948
- PMCID: PMC9950780
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1088288
Roxadustat, a HIF-PHD inhibitor with exploitable potential on diabetes-related complications
Abstract
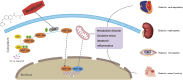
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic diseases caused by absolute or relative deficiency of insulin secretion and characterized by chronic hyperglycemia. Its complications affect almost every tissue of the body, usually leading to blindness, renal failure, amputation, etc. and in the final stage, it mostly develops into cardiac failure, which is the main reason why diabetes mellitus manifests itself as a high clinical lethality. The pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and its complications involves various pathological processes including excessive production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and metabolic imbalance. Hypoxia-inducible Factor (HIF) signaling pathway plays an important role in both of the above processes. Roxadustat is an activator of Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1α, which increases the transcriptional activity of Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1α by inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase (HIF-PHD). Roxadustat showed regulatory effects on maintaining metabolic stability in the hypoxic state of the body by activating many downstream signaling pathways such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), glucose transporter protein-1 (GLUT1), lactate dehydrogenase (LDHA), etc. This review summarizes the current research findings of roxadustat on the diseases of cardiomyopathy, nephropathy, retinal damage and impaired wound healing, which also occur at different stages of diabetes and greatly contribute to the damage caused by diabetes to the organism. We attempts to uncover a more comprehensive picture of the therapeutic effects of roxadustat, and inform its expanding research about diabetic complications treatment.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM); diabetic nephropathy; hypoxia-inducible factor; roxadustat.
Copyright © 2023 Fang, Ma, Zhang, Sun and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway by roxadustat improves glucose metabolism in human primary myotubes from men.Diabetologia. 2024 Sep;67(9):1943-1954. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06185-6. Epub 2024 May 30. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 38814443 Free PMC article.
-
Roxadustat promotes angiogenesis through HIF-1α/VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling and accelerates cutaneous wound healing in diabetic rats.Wound Repair Regen. 2019 Jul;27(4):324-334. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12708. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Wound Repair Regen. 2019. PMID: 30817065
-
Repression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 contributes to increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in diabetes.Elife. 2022 Feb 15;11:e70714. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70714. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35164902 Free PMC article.
-
Mutual Antagonism of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Isoforms in Cardiac, Vascular, and Renal Disorders.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2020 Sep 28;5(9):961-968. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2020.05.006. eCollection 2020 Sep. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 33015417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disturbed hypoxic responses as a pathogenic mechanism of diabetic foot ulcers.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016 Jan;32 Suppl 1:179-85. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2742. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016. PMID: 26453314 Review.
Cited by
-
Response to "Roxadustat: More Than an Erythropoietic Agent?".Kidney Int Rep. 2024 Oct 28;10(1):276. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.10.020. eCollection 2025 Jan. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 39810786 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The ROX@PDA@PCL vascularized bionic nerve conduit facilitates the restoration of nerve defects.Front Neurol. 2025 May 13;16:1561177. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1561177. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40433608 Free PMC article.
-
High glucose/ChREBP-induced Hif-1α transcriptional activation in CD4+ T cells reduces the risk of diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting the Th1 response.Diabetologia. 2025 May;68(5):1044-1056. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06354-7. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Diabetologia. 2025. PMID: 39885014 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular and renal safety outcomes of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor roxadustat for anemia patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(1):2313864. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2313864. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38345037 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway by roxadustat improves glucose metabolism in human primary myotubes from men.Diabetologia. 2024 Sep;67(9):1943-1954. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06185-6. Epub 2024 May 30. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 38814443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akizawa T., Iwasaki M., Yamaguchi Y., Majikawa Y., Reusch M. (2020a). Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, active-comparator (darbepoetin alfa) study of oral roxadustat in CKD patients with anemia on hemodialysis in Japan. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 31, 1628–1639. 10.1681/ASN.2019060623 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

