Nucleolin recognizing silica nanoparticles inhibit cell proliferation by activating the Bax/Bcl-2/caspase-3 signalling pathway to induce apoptosis in liver cancer
- PMID: 36843953
- PMCID: PMC9947157
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1117052
Nucleolin recognizing silica nanoparticles inhibit cell proliferation by activating the Bax/Bcl-2/caspase-3 signalling pathway to induce apoptosis in liver cancer
Abstract
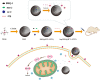
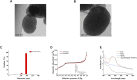
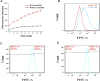
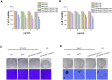
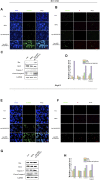
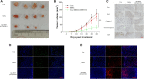
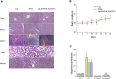
Multifunctional nanocarrier platforms have shown great potential for the diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer. Here, a novel nucleolin-responsive nanoparticle platform was constructed for the concurrent detection of nucleolin and treatment of liver cancer. The incorporation of AS1411 aptamer, icaritin (ICT) and FITC into mesoporous silica nanoparticles, labelled as Atp-MSN (ICT@FITC) NPs, was the key to offer functionalities. The specific combination of the target nucleolin and AS1411 aptamer caused AS1411 to separate from mesoporous silica nanoparticles surface, allowing FITC and ICT to be released. Subsequently, nucleolin could be detected by monitoring the fluorescence intensity. In addition, Atp-MSN (ICT@FITC) NPs can not only inhibit cell proliferation but also improve the level of ROS while activating the Bax/Bcl-2/caspase-3 signalling pathway to induce apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, our results demonstrated that Atp-MSN (ICT@FITC) NPs had low toxicity and could induce CD3+ T-cell infiltration. As a result, Atp-MSN (ICT@FITC) NPs may provide a reliable and secure platform for the simultaneous identification and treatment of liver cancer.
Keywords: AS1411; MSNs; apoptosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; proliferation.
Copyright © 2023 Xiang, Li, Gu, Li, Li, Li and Yi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted rod-shaped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the co-delivery of camptothecin and survivin shRNA in to colon adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020 Nov;156:84-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.08.026. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020. PMID: 32882423
-
A nucleolin-targeted multimodal nanoparticle imaging probe for tracking cancer cells using an aptamer.J Nucl Med. 2010 Jan;51(1):98-105. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.069880. Epub 2009 Dec 15. J Nucl Med. 2010. PMID: 20008986
-
Cell Surface Nucleolin as a Promising Receptor for Effective AS1411 Aptamer-Mediated Targeted Drug Delivery into Cancer Cells.Curr Drug Deliv. 2018;15(9):1323-1329. doi: 10.2174/1567201815666180724104451. Curr Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 30039760
-
Anti-nucleolin aptamer AS1411: an advancing therapeutic.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Sep 21;10:1217769. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1217769. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37808518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-quadruplex oligonucleotide AS1411 as a cancer-targeting agent: Uses and mechanisms.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 May;1861(5 Pt B):1414-1428. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.12.015. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 28007579 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicine with nano-delivery systems for tumor immunotherapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 17;23(1):357. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03378-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40382641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamer-functionalized nanomaterials (AFNs) for therapeutic management of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 May 12;22(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02486-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38735927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-binding proteins as therapeutic targets in cancer.RNA Biol. 2025 Dec;22(1):1-8. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2025.2470511. Epub 2025 Feb 27. RNA Biol. 2025. PMID: 40016176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TfR Aptamer-Functionalized MSNs for Enhancing Targeted Cellular Uptake and Therapy of Cancer Cells.ACS Omega. 2023 Dec 12;8(51):48975-48983. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c06562. eCollection 2023 Dec 26. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38162791 Free PMC article.
-
Natural anti-cancer products: insights from herbal medicine.Chin Med. 2025 Jun 9;20(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01124-y. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40490812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

