Application of proteomics to determine the mechanism of ozone on sweet cherries (Prunus avium L.) by time-series analysis
- PMID: 36844069
- PMCID: PMC9948404
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1065465
Application of proteomics to determine the mechanism of ozone on sweet cherries (Prunus avium L.) by time-series analysis
Abstract
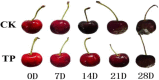
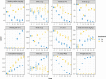
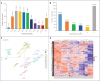
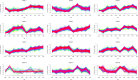
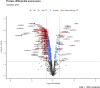
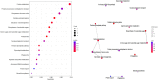
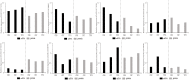
This research investigated the mechanism of ozone treatment on sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) by Lable-free quantification proteomics and physiological traits. The results showed that 4557 master proteins were identified in all the samples, and 3149 proteins were common to all groups. Mfuzz analyses revealed 3149 candidate proteins. KEGG annotation and enrichment analysis showed proteins related to carbohydrate and energy metabolism, protein, amino acids, and nucleotide sugar biosynthesis and degradation, and fruit parameters were characterized and quantified. The conclusions were supported by the fact that the qRT-PCR results agreed with the proteomics results. For the first time, this study reveals the mechanism of cherry in response to ozone treatment at a proteome level.
Keywords: label-free quantification proteomics; mfuzz; ozone; preservation; sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.).
Copyright © 2023 Zhao, Hou, Zhang, Ji, Dong, Yu, Chen, Chen and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Calle A., Serradilla M. J., Wunsch A. (2021). QTL mapping of phenolic compounds and fruit colour in sweet cherry using a 6+9K SNP array genetic map. Sci. Hortic. 280, 109900. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.109900 - DOI
-
- FDA (2001). Secondary direct food additives permitted in food for human consumption, final rule. Fed. Regist. 66, 33829–33820.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

