Can circulating oxidative stress-related biomarkers be used as an early prognostic marker for COVID-19?
- PMID: 36844214
- PMCID: PMC9948026
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1041115
Can circulating oxidative stress-related biomarkers be used as an early prognostic marker for COVID-19?
Abstract
Background: Oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis of many diseases. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and oxidative stress and the severity of the disease in new COVID-19 patients, and, to compare the levels of NF-κB, oxidized LDL (oxLDL), and lectin-like oxidized-LDL receptor-1 (LOX-1) with oxygen saturation, which is an indicator of the severity parameters of the disease in COVID-19 patients.
Methods: In this prospective study, 100 COVID-19 patients and 100 healthy subjects were selected.
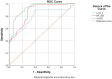
Results: LOX-1, NF-κB, and oxLDL were found to be higher in COVID-19 patients compared to the healthy subjects (p < 0.001 for all). According to the results of correlation analysis, it was found that there was no significant relationship between oxygen saturation and LOX-1, NF-κB and oxLDL parameters. There was significant relationship between oxLDL with LOX-1 and NF-κB in patients with COVID-19 disease. ROC analysis results of the highest discrimination power were oxLDL (AUC: 0.955, CI: 0.904-1.000; sensitivity: 77%, and specificity: 100%, for cutoff: 127.944 ng/l) indicating COVID-19.
Conclusion: Oxidative stress plays an essential role in COVID-19. NF-κB, oxLDL, and LOX-1 seem to represent good markers in COVID-19. Our study also showed that oxLDL has the highest power in distinguishing patients with COVID-19 from the healthy subjects.
Keywords: COVID-19; lectin-like oxidized-LDL receptor-1; lipid metabolism; nuclear factor kappa B; oxidized LDL.
Copyright © 2023 Uysal, Yüksel, Durmus, Cuhadaroglu, Gelisgen and Uzun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous