Open-Source Chromatographic Data Analysis for Reaction Optimization and Screening
- PMID: 36844498
- PMCID: PMC9951288
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.2c01042
Open-Source Chromatographic Data Analysis for Reaction Optimization and Screening
Abstract
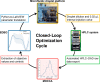
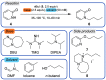
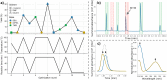
Automation and digitalization solutions in the field of small molecule synthesis face new challenges for chemical reaction analysis, especially in the field of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Chromatographic data remains locked in vendors' hardware and software components, limiting their potential in automated workflows and data science applications. In this work, we present an open-source Python project called MOCCA for the analysis of HPLC-DAD (photodiode array detector) raw data. MOCCA provides a comprehensive set of data analysis features, including an automated peak deconvolution routine of known signals, even if overlapped with signals of unexpected impurities or side products. We highlight the broad applicability of MOCCA in four studies: (i) a simulation study to validate MOCCA's data analysis features; (ii) a reaction kinetics study on a Knoevenagel condensation reaction demonstrating MOCCA's peak deconvolution feature; (iii) a closed-loop optimization study for the alkylation of 2-pyridone without human control during data analysis; (iv) a well plate screening of categorical reaction parameters for a novel palladium-catalyzed cyanation of aryl halides employing O-protected cyanohydrins. By publishing MOCCA as a Python package with this work, we envision an open-source community project for chromatographic data analysis with the potential of further advancing its scope and capabilities.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
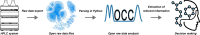






Similar articles
-
Combined use of liquid chromatography-hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC-QTOF-MS) and high performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detector (HPLC-DAD) in systematic toxicological analysis.Forensic Sci Int. 2011 Oct 10;212(1-3):215-26. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2011.06.014. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Forensic Sci Int. 2011. PMID: 21764531
-
Intelligent peak deconvolution through in-depth study of the data matrix from liquid chromatography coupled with a photo-diode array detector applied to pharmaceutical analysis.J Chromatogr A. 2016 Oct 21;1469:35-47. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2016.09.037. Epub 2016 Sep 19. J Chromatogr A. 2016. PMID: 27712885
-
Skyline for Small Molecules: A Unifying Software Package for Quantitative Metabolomics.J Proteome Res. 2020 Apr 3;19(4):1447-1458. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00640. Epub 2020 Mar 26. J Proteome Res. 2020. PMID: 31984744 Free PMC article.
-
Critical review on data processing algorithms in non-target screening: challenges and opportunities to improve result comparability.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Jul;415(18):4111-4123. doi: 10.1007/s00216-023-04776-7. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37380744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Forced degradation and impurity profiling: recent trends in analytical perspectives.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Dec;86:11-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23969330 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical Process Development in the Pharmaceutical Industry in Europe-Insights and Perspectives from Industry Scientists.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 May;64(19):e202420719. doi: 10.1002/anie.202420719. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 40145815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parallel multi-droplet platform for reaction kinetics and optimization.Chem Sci. 2023 Aug 4;14(33):8798-8809. doi: 10.1039/d3sc02082g. eCollection 2023 Aug 23. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37621435 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Driving Laboratories for Chemistry and Materials Science.Chem Rev. 2024 Aug 28;124(16):9633-9732. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00055. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39137296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calibration-free reaction yield quantification by HPLC with a machine-learning model of extinction coefficients.Chem Sci. 2024 May 29;15(26):10092-10100. doi: 10.1039/d4sc01881h. eCollection 2024 Jul 3. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38966367 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging trends in the optimization of organic synthesis through high-throughput tools and machine learning.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2025 Jan 6;21:10-38. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.21.3. eCollection 2025. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2025. PMID: 39811684 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andersson S.; Armstrong A.; Björe A.; Bowker S.; Chapman S.; Davies R.; Donald C.; Egner B.; Elebring T.; Holmqvist S.; Inghardt T.; Johannesson P.; Johansson M.; Johnstone C.; Kemmitt P.; Kihlberg J.; Korsgren P.; Lemurell M.; Moore J.; Pettersson J. A.; Pointon H.; Pontén F.; Schofield P.; Selmi N.; Whittamore P. Making Medicinal Chemistry More Effective-Application of Lean Sigma to Improve Processes, Speed and Quality. Drug Discovery Today 2009, 14 (11–12), 598–604. 10.1016/j.drudis.2009.03.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marion P.; Bernela B.; Piccirilli A.; Estrine B.; Patouillard N.; Guilbot J.; Jérôme F. Sustainable Chemistry: How to Produce Better and More from Less?. Green Chem. 2017, 19 (21), 4973–4989. 10.1039/C7GC02006F. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

