Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Antimicrobial Components and LC/QToF Profile of Plumeria obtusa: Potential for the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistance
- PMID: 36844537
- PMCID: PMC9947952
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c06803
Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Antimicrobial Components and LC/QToF Profile of Plumeria obtusa: Potential for the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistance
Abstract
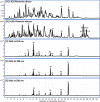
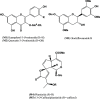
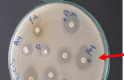
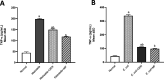
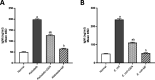
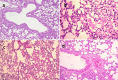
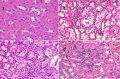
The methanolic fraction (M-F) of the total extract (TE) of Plumeria obtusa L. aerial parts showed promising antibacterial effects against the MDR (multidrug-resistant) gram-negative pathogens Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli O157:H7 [Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC)]. In addition, M-F had a synergistic effect (in combination with vancomycin) against the MDR gram-positive strains MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) and Bacillus cereus. After treating the K. pneumoniae- and STEC-infected mice with M-F (25 mg/kg, i.p.), the level of IgM and TNF-α was decreased and the severity of pathological lesions were reduced better than that observed after administration of gentamycin (33 mg/kg, i.p.). Thirty-seven compounds including 10 plumeria-type iridoids and 18 phenolics, 7 quinoline derivatives, 1 amino acid, and 1 fatty acid were identified in TE using LC/ESI-QToF. Furthermore, five compounds; kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside (M1), quercetin 3-O-rutinoside (M2), glochiflavanoside B (M3), plumieride (M4), and 13-O-caffeoylplumieride (M5) were isolated from M-F. M5 was active against K. pneumoniae (MIC of 64 μg/mL) and STEC (MIC of 32 μg/mL). These findings suggested that M-F and M5 are promising antimicrobial natural products for combating MDR K. pneumoniae and STEC nosocomial infections.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kraker M. E. A. D. Burden of disease associated with antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 398–407. - PubMed
-
- Al Salman J.; Al Dabal L.; Bassetti M.; Alfouzan W. A.; Al Maslamani M.; Alraddadi B.; Elhoufi A.; Enani M.; Khamis F. A.; Mokkadas E.; et al. Management of infections caused by WHO critical priority Gram-negative pathogens in Arab countries of the Middle East: a consensus paper. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, e106104 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106104. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fawazy N. G.; Panda S. S.; Mostafa A.; Kariuki B. M.; Bekheit M. S.; Moatasim Y.; Kutkat O.; Fayad W.; El-Manawaty M. A.; Soliman A.; et al. Development of spiro-3-indolin-2-one containing compounds of antiproliferative and anti-SARS-CoV-2 properties. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–21. 10.1038/s41598-022-17883-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

