A GENERAL RETURN-MAPPING FRAMEWORK FOR FRACTIONAL VISCO-ELASTO-PLASTICITY
- PMID: 36844810
- PMCID: PMC9967175
- DOI: 10.3390/fractalfract6120715
A GENERAL RETURN-MAPPING FRAMEWORK FOR FRACTIONAL VISCO-ELASTO-PLASTICITY
Abstract
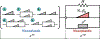
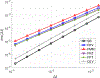
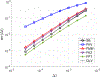
We develop a fractional return-mapping framework for power-law visco-elasto-plasticity. In our approach, the fractional viscoelasticity is accounted through canonical combinations of Scott-Blair elements to construct a series of well-known fractional linear viscoelastic models, such as Kelvin-Voigt, Maxwell, Kelvin-Zener and Poynting-Thomson. We also consider a fractional quasi-linear version of Fung's model to account for stress/strain nonlinearity. The fractional viscoelastic models are combined with a fractional visco-plastic device, coupled with fractional viscoelastic models involving serial combinations of Scott-Blair elements. We then develop a general return-mapping procedure, which is fully implicit for linear viscoelastic models, and semi-implicit for the quasi-linear case. We find that, in the correction phase, the discrete stress projection and plastic slip have the same form for all the considered models, although with different property and time-step dependent projection terms. A series of numerical experiments is carried out with analytical and reference solutions to demonstrate the convergence and computational cost of the proposed framework, which is shown to be at least first-order accurate for general loading conditions. Our numerical results demonstrate that the developed framework is more flexible, preserves the numerical accuracy of existing approaches while being more computationally tractable in the visco-plastic range due to a reduction of 50% in CPU time. Our formulation is especially suited for emerging applications of fractional calculus in bio-tissues that present the hallmark of multiple viscoelastic power-laws coupled with visco-plasticity.
Keywords: fast convolution; fractional quasi-linear viscoelasticity; power-law visco-elasto-plasticity.
Figures
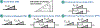
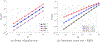


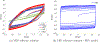
References
-
- BLAIR G, VEINOGLOU B, AND CAFFYN B, Limitations of the newtonian time scale in relation to non-equilibrium rheological states and a theory of quasi-properties, Proc R Soc A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 189 (1947), pp. 69–87. - PubMed
-
- Bonadkar N, Gerum R, Kuhn M, Sporer M, Lippert A, Schneider W, AifanTIS K, AND FABRY B, Mechanical plasticity of cells, Nature materials, 15 (2016), pp. 1090 – 1094. - PubMed
-
- BONFANTI A, KAPLAN JL, CHARRAS G, AND KABLA AJ, Fractional viscoelastic models for power-law materials, Soft Matter, (2020). - PubMed
-
- Branco A, Todorovic Fabro A, GoNçALVES TM , AND Garcia Martins RH, Alterations in extracellular matrix composition in the aging larynx, Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, 152 (2015), pp. 302–307. - PubMed
-
- Choi J-S, Kim NJ, Klemuk S, Jang YH, Park IS, Ahn KH, Lim J-Y , AND KIM Y-M, Preservation of viscoelastic properties of rabbit vocal folds after implantation of hyaluronic acid-based biomaterials, Otolaryngology–head and neck surgery, 147 (2012), pp. 515–521. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
