Effect of Tocilizumab on "Ventilator Free Days" Composite Outcome in SARS-CoV-2 Patients: A Retrospective Competing Risk Analysis
- PMID: 36844963
- PMCID: PMC9949015
- DOI: 10.2478/rjaic-2022-0001
Effect of Tocilizumab on "Ventilator Free Days" Composite Outcome in SARS-CoV-2 Patients: A Retrospective Competing Risk Analysis
Abstract
Background: SARS-CoV-2 infection demonstrates a wide range of severity. More severe cases demonstrate a cytokine storm with elevated serum interleukin-6, hence IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab was tried for the management of severe cases.
Aims: Effect of tocilizumab on ventilator-free days among critically ill SARS-CoV-2 patients.
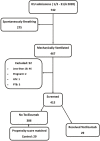
Method: Retrospective propensity score matching study, comparing mechanically ventilated patients who received tocilizumab to a control group.
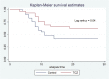
Results: 29 patients in the intervention group were compared to 29 controls. Matched groups were similar. Ventilator-free days were more numerous in the intervention group (SHR 2.7, 95% CI: 1.2 - 6.3; p = 0.02), ICU mortality rate was not different (37.9% versus 62%, p = 0.1), actual ventilator-free periods were significantly longer in tocilizumab group (mean difference 4.7 days; p = 0.02). Sensitivity analysis showed a significantly lower hazard ratio of death in tocilizumab group (HR 0.49, 95% CI: 0.25 - 0.97; p = 0.04). There was no difference in positive cultures among groups (55.2% in tocilizumab group versus 34.5% in the control; p = 0.1).
Conclusion: Tocilizumab may improve the composite outcome of ventilator-free days at day 28 among mechanically ventilated SARS-CoV-2 patients; it is associated with significantly longer actual ventilator-free periods, and insignificantly lower mortality and higher superinfection.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; tocilizumab; ventilator-free days.
© 2022 Ahmed F. Mady et al., published by Sciendo.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019. [accessed 15 October 2020].
-
- Aletreby WT, Alharthy AM, Faqihi F, Mady AF, Ramadan OE, Huwait BM. et al. Dynamics of SARS CoV-2 outbreak in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: A predictive model. Saudi Crit Care J. 2020;4:79–83. doi: 10.4103/sccj.sccj_19_20. - DOI
-
- Mady A, Aletreby W, Abdulrahman B, Lhmdi M, Noor AM, Alqahtani SA, Soliman I, Alharthy A, Karakitsos D, Memish ZA. Tocilizumab in the treatment of rapidly evolving COVID-19 pneumonia and multifaceted critical illness: A retrospective case series. Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2020 Dec;60:417–424. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2020.10.061. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous