Acute heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) without thrombocytopenia post aortocoronary bypass grafting
- PMID: 36844968
- PMCID: PMC9942017
- DOI: 10.1007/s12055-023-01494-8
Acute heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) without thrombocytopenia post aortocoronary bypass grafting
Abstract
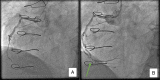
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) after cardiac surgery is a clinical condition associated with increased incidence of thromboembolic events and mortality. HIT without thrombocytopenia is a rare clinical entity poorly reported in the literature, especially after cardiac surgery. In this case report, we present the case of a post aortocoronary bypass grafting patient who presented with HIT in the absence of thrombocytopenia.
Keywords: Anti-heparin antibody; Graft thrombosis; HIT without thrombocytopenia; Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
© Indian Association of Cardiovascular-Thoracic Surgeons 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNone declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
