The association of vitamin D status with oxidative stress biomarkers and matrix metalloproteinases in patients with knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 36845046
- PMCID: PMC9944738
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1101516
The association of vitamin D status with oxidative stress biomarkers and matrix metalloproteinases in patients with knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objective: The association of vitamin D status with osteoarthritis (OA) has been demonstrated previously. The current study was performed to examine the association of vitamin D status with oxidative stress markers and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in patients with knee OA.
Methods: This case-control study was conducted on 124 subjects with mild to moderate knee OA and 65 healthy controls. Demographic data was collected from all participants at baseline. Serum levels of vitamin D as well as markers of oxidative stress including malondialdehyde (MDA), total oxidant status (TOS), superoxide dismutase (SOD), oxidative stress index (OSI), paraoxonase-1 (PON-1), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), catalase (CAT), and total antioxidant capacity (TAC) were evaluated for each participant. Furthermore, serum concentrations of MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13, and cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) were measured.
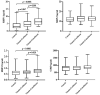
Results: The results of the present study indicated that individuals with vitamin D insufficiency had higher levels of MDA, TOS, SOD, and OSI as well as lower levels of PON-1 and TAC. Based on the linear regression analysis, serum vitamin D levels were inversely correlated with MDA, TOS, SOD, OSI, MMP-1, and MMP-13 and positively associated with TAC levels (p < 0.0001). Patients with sufficient vitamin D levels had lower MMP-1 and MMP-13 levels compared to patients with vitamin D insufficiency (p < 0.001 and p < 0.001, respectively).
Conclusion: Findings from this study showed a strong association between vitamin D deficiency and increased oxidative stress and MMPs activity in patients with knee OA.
Keywords: clinical; knee osteoarthritis; nutrition; oxidative stress; vitamin D.
Copyright © 2023 Amirkhizi, Ghoreishy, Baker, Hamedi-Shahraki and Asghari.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

