Formation mechanism and functional properties of walnut protein isolate and soy protein isolate nanoparticles using the pH-cycle technology
- PMID: 36845052
- PMCID: PMC9950265
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1135048
Formation mechanism and functional properties of walnut protein isolate and soy protein isolate nanoparticles using the pH-cycle technology
Abstract
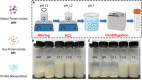
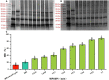
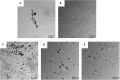
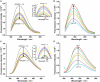
Walnut protein isolate (WPI) is a nutritious protein with poor solubility, which severely limits its application. In this study, composite nanoparticles were prepared from WPI and soy protein isolate (SPI) using the pH-cycle technology. The WPI solubility increased from 12.64 to 88.53% with a WPI: SPI ratio increased from 1: 0.01 to 1: 1. Morphological and structural analyses illustrated that interaction forces with hydrogen bonding as the main effect jointly drive the binding of WPI to SPI and that protein co-folding occurs during the neutralization process, resulting in a hydrophilic rigid structure. In addition, the interfacial characterization showed that the composite nanoparticle with a large surface charge enhanced the affinity with water molecules, prevented protein aggregation, and protected the new hydrophilic structure from damage. All these parameters helped to maintain the stability of the composite nanoparticles in a neutral environment. Amino acid analysis, emulsification capacity, foaming, and stability analysis showed that the prepared WPI-based nanoparticles exhibited good nutritional and functional properties. Overall, this study could provide a technical reference for the value-added use of WPI and an alternative strategy for delivering natural food ingredients.
Keywords: functional properties; interaction; nanoparticles; pH-cycle; soy protein isolate; walnut protein isolate.
Copyright © 2023 Dai, Xu, Shi, Liu and Bi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

