Immunity of turbot Induced by inactivated vaccine of Aeromonas salmonicida from the perspective of DNA methylation
- PMID: 36845093
- PMCID: PMC9945314
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1124322
Immunity of turbot Induced by inactivated vaccine of Aeromonas salmonicida from the perspective of DNA methylation
Abstract
Introduction: DNA methylation was one of the most important modification in epigenetics and played an important role in immune response. Since the introduction of Scophthalmus maximus, the scale of breeding has continued to expand, during which diseases caused by various bacteria, viruses and parasites have become increasingly serious. Therefore, the inactivated vaccines have been widely researched and used in the field of aquatic products with its unique advantages. However, the immune mechanism that occurred in turbot after immunization with inactivated vaccine of Aeromonas salmonicida was not clear.
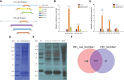
Methods: In this study, differentially methylated regions (DMRs) were screened by Whole Genome Bisulfite Sequencing (WGBS) and significantly differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened by Transcriptome sequencing. Double luciferase report assay and DNA pull-down assay were further verified the DNA methylation state of the gene promoter region affected genes transcriptional activity after immunization with inactivated vaccine of Aeromonas salmonicida.
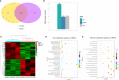
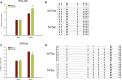
Results: A total of 8149 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) were screened, in which there were many immune-related genes with altered DNA methylation status. Meanwhile, 386 significantly differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified, many of which were significantly enriched in Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway and C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway. Combined analysis of WGBS results and RNA-seq results, a total of 9 DMRs of negatively regulated genes are located in the promoter region, including 2 hypermethylated genes with lower expression and 7 hypomethylated genes with higher expression. Then, two immune-related genes C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1-like (C5ar1-Like) and Eosinophil peroxidase-like (EPX-Like), were screened to explore the regulation mechanism of DNA methylation modification on their expression level. Moreover, the DNA methylation state of the gene promoter region affected genes transcriptional activity by inhibiting the binding of transcription factors, which lead to changes in the expression level of the gene.
Discussion: We jointly analyzed WGBS and RNA-seq results and revealed the immune mechanism that occurred in turbot after immunized with inactivated vaccine of A. salmonicida from the perspective of DNA methylation.
Keywords: Aeromonas salmonicida; DNA methylation; Scophthalmus maximus; Whole Genome Bisulfite Sequencing; inactivated vaccine; transcriptome sequencing.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Su, Liu, Guo, Zhou and Xiu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) kidney responses to inactivated bivalent vaccine against Aeromonas salmonicida and Edwardsiella tarda.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023 Dec;143:109174. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.109174. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37858783
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals deep insights into the early immune response of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) induced by inactivated Aeromonas salmonicida vaccine.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021 Dec;119:163-172. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2021.09.027. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34562583
-
Unravelling turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) resistance to Aeromonas salmonicida: transcriptomic insights from two full-sibling families with divergent susceptibility.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 6;15:1522666. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1522666. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39712009 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of bivalent vaccine against Aeromonas salmonicida and Edwardsiella tarda infections in turbot.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023 Aug;139:108837. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.108837. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37269913
-
A compound ginseng stem leaf saponins and aluminium adjuvant enhances the potency of inactivated Aeromonas salmonicida vaccine in turbot.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022 Sep;128:60-66. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.07.027. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35843529
References
-
- Hu Q, Ao Q, Tan Y, Gan X, Luo Y, Zhu J. Genome-wide DNA methylation and rna analysis reveal potential mechanism of resistance to streptococcus agalactiae in gift strain of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus ). J Immunol (Baltimore Md 1950) (2020) 204(12):3182–90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901496 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

