Specific in situ immuno-imaging of pulmonary-resident memory lymphocytes in human lungs
- PMID: 36845117
- PMCID: PMC9951616
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1100161
Specific in situ immuno-imaging of pulmonary-resident memory lymphocytes in human lungs
Abstract
Introduction: Pulmonary-resident memory T cells (TRM) and B cells (BRM) orchestrate protective immunity to reinfection with respiratory pathogens. Developing methods for the in situ detection of these populations would benefit both research and clinical settings.
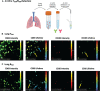
Methods: To address this need, we developed a novel in situ immunolabelling approach combined with clinic-ready fibre-based optical endomicroscopy (OEM) to detect canonical markers of lymphocyte tissue residency in situ in human lungs undergoing ex vivo lung ventilation (EVLV).
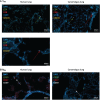
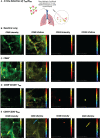
Results: Initially, cells from human lung digests (confirmed to contain TRM/BRM populations using flow cytometry) were stained with CD69 and CD103/CD20 fluorescent antibodies and imaged in vitro using KronoScan, demonstrating it's ability to detect antibody labelled cells. We next instilled these pre-labelled cells into human lungs undergoing EVLV and confirmed they could still be visualised using both fluorescence intensity and lifetime imaging against background lung architecture. Finally, we instilled fluorescent CD69 and CD103/CD20 antibodies directly into the lung and were able to detect TRM/BRM following in situ labelling within seconds of direct intra-alveolar delivery of microdoses of fluorescently labelled antibodies.
Discussion: In situ, no wash, immunolabelling with intra-alveolar OEM imaging is a novel methodology with the potential to expand the experimental utility of EVLV and pre-clinical models.
Keywords: fluorescence lifetime imaging; lung; optical endomicroscopy; resident memory B cells; resident memory T cells.
Copyright © 2023 Humphries, O’Connor, Stewart, Quinn, Gaughan, Mills, Williams, Stone, Finlayson, Chabaud-Riou, Boudet, Dhaliwal and Pavot.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors DH, MC-R, FB and VP were employed by company Sanofi. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare that this study received funding from Sanofi. The funder had the following involvement in the study: study design, data analysis, decision to publish, and preparation of the manuscript.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

