The effectiveness of real-time computer-aided and quality control systems in colorectal adenoma and polyp detection during colonoscopies: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 36845807
- PMCID: PMC9949794
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000079
The effectiveness of real-time computer-aided and quality control systems in colorectal adenoma and polyp detection during colonoscopies: a meta-analysis
Abstract
This meta-analysis aims to quantify the effectiveness of artificial intelligence (AI)-supported colonoscopy compared to standard colonoscopy in adenoma detection rate (ADR) differences with the use of computer-aided detection and quality control systems. Moreover, the polyp detection rate (PDR) intergroup differences and withdrawal times will be analyzed.
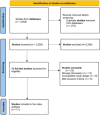
Methods: This study was conducted adhering to PRISMA guidelines. Studies were searched across PubMed, CINAHL, EMBASE, Scopus, Cochrane, and Web of Science. Keywords including the following 'Artificial Intelligence, Polyp, Adenoma, Detection, Rate, Colonoscopy, Colorectal, Colon, Rectal' were used. Odds ratio (OR) applying 95% CI for PDR and ADR were computed. SMD with 95% CI for withdrawal times were computed using RevMan 5.4.1 (Cochrane). The risk of bias was assessed using the RoB 2 tool.
Results: Of 2562 studies identified, 11 trials were included comprising 6856 participants. Of these, 57.4% participants were in the AI group and 42.6% individuals were in in the standard group. ADR was higher in the AI group compared to the standard of care group (OR=1.51, P=0.003). PDR favored the intervened group compared to the standard group (OR=1.89, P<0.0001). A medium measure of effect was found for withdrawal times (SMD=0.25, P<0.0001), therefore with limited practical applications.
Conclusion: AI-supported colonoscopies improve PDR and ADR; however, no noticeable worsening of withdrawal times is noted. Colorectal cancers are highly preventable if diagnosed early-on. With AI-assisted tools in clinical practice, there is a strong potential to reduce the incidence rates of cancers in the near future.
Keywords: adenoma; colorectal; meta-analysis; polyps; trials; withdrawal time.
© 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of artificial intelligence-aided colonoscopy for adenoma and polyp detection: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2022 Mar;37(3):495-506. doi: 10.1007/s00384-021-04062-x. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2022. PMID: 34762157 Review.
-
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Improving Polyp and Adenoma Detection Rate During Colonoscopy: Systematic-Review and Meta-Analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Nov 1;24(11):3655-3663. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.11.3655. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 38019222 Free PMC article.
-
One-year review of real-time artificial intelligence (AI)-aided endoscopy performance.Surg Endosc. 2023 Aug;37(8):6402-6407. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-09979-8. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 36932187
-
Effect of computer-aided colonoscopy on adenoma miss rates and polyp detection: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Feb;38(2):162-176. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16059. Epub 2022 Dec 11. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36350048
-
Artificial Intelligence-Aided Colonoscopy for Polyp Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2021 Oct;31(10):1143-1149. doi: 10.1089/lap.2020.0777. Epub 2021 Feb 1. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2021. PMID: 33524298
Cited by
-
Colonoscopy Remains an Important Option for Primary Screening for Colorectal Cancer.Dig Dis Sci. 2025 May;70(5):1595-1605. doi: 10.1007/s10620-024-08760-8. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Dig Dis Sci. 2025. PMID: 39666212 Review.
-
Effect of computer aided detection device on the adenoma detection rate and serrated detection rate among trainee fellows.JGH Open. 2024 Sep 9;8(9):e70018. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.70018. eCollection 2024 Sep. JGH Open. 2024. PMID: 39253018 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence for colorectal neoplasia detection during colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.EClinicalMedicine. 2023 Nov 30;66:102341. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102341. eCollection 2023 Dec. EClinicalMedicine. 2023. PMID: 38078195 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Computer-aided Detection Technology in Adenoma Detection Rate Among Experienced Endoscopists in the Community Setting.J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2024 Sep 9;14(5):42-48. doi: 10.55729/2000-9666.1396. eCollection 2024. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2024. PMID: 39399190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rex DK. Can we do resect and discard with artificial intelligence-assisted colon polyp “optical biopsy?,”. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc 2020;22:52–55.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
