Association of chronic non-cancer pain status and buprenorphine treatment retention among individuals with opioid use disorder: Results from electronic health record data
- PMID: 36845986
- PMCID: PMC9948869
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dadr.2022.100048
Association of chronic non-cancer pain status and buprenorphine treatment retention among individuals with opioid use disorder: Results from electronic health record data
Abstract
Background: Although chronic non-cancer pain (CNCP) is common among individuals with opioid use disorder (OUD), its impact on buprenorphine treatment retention is unclear. The goal of this study was to use electronic health record (EHR) data to examine the association of CNCP status and 6-month buprenorphine retention among patients with OUD.
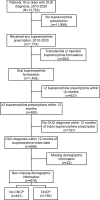
Methods: We analyzed EHR data of patients with OUD who received buprenorphine treatment in an academic healthcare system between 2010 and 2020 (N = 676). We used Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional hazards regression to estimate risk of buprenorphine treatment discontinuation (≥90 days between subsequent prescriptions). We used Poisson regression to estimate the association of CNCP and the number of buprenorphine prescriptions over 6 months.
Results: Compared to those without CNCP, a higher proportion of patients with CNCP were of older age and had comorbid diagnoses for psychiatric and substance use disorders. There were no differences in the probability of buprenorphine treatment continuation over 6 months by CNCP status (p = 0.15). In the adjusted cox regression model, the presence of CNCP was not associated with time to buprenorphine treatment discontinuation (HR = 0.90, p = 0.28). CNCP status was associated with a higher number of prescriptions over 6 months (IRR = 1.20, p < 0.01).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that the presence of CNCP alone cannot be reliably associated with buprenorphine retention in patients with OUD. Nonetheless, providers should be aware of the association between CNCP and greater psychiatric comorbidity among patients with OUD when developing treatment plans. Research on the influence of additional characteristics of CNCP on treatment retention is needed.
Keywords: Buprenorphine; Chronic pain; Opioid use disorder.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Li-Tzy Wu also has received research funding from Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. William S. John also has received research funding from Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Paolo Mannelli has received research support from Alkermes Inc. and Orexo, and is a consultant for Alkermes, Intracellular Therapies, Atai Life Sciences, and Guidepoint Global. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Current Pain Status on Low-Barrier Buprenorphine Treatment Response Among Patients with Opioid Use Disorder.Pain Med. 2021 May 21;22(5):1205-1212. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnab058. Pain Med. 2021. PMID: 33585885 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived social support in patients with chronic pain with and without opioid use disorder and role of medication for opioid use disorder.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021 Apr 1;221:108619. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2021.108619. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021. PMID: 33667781 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable naltrexone, oral naltrexone, and buprenorphine utilization and discontinuation among individuals treated for opioid use disorder in a United States commercially insured population.J Subst Abuse Treat. 2018 Feb;85:90-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2017.07.001. Epub 2017 Jul 3. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2018. PMID: 28733097 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for discontinuation of buprenorphine treatment for opioid use disorders in a multi-state sample of Medicaid enrollees.J Subst Abuse Treat. 2018 Dec;95:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Sep 7. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2018. PMID: 30352671 Free PMC article.
-
Prior National Drug Abuse Treatment Clinical Trials Network (CTN) opioid use disorder trials as background and rationale for NIDA CTN-0100 "optimizing retention, duration and discontinuation strategies for opioid use disorder pharmacotherapy (RDD)".Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2021 Mar 6;16(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13722-021-00223-z. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 33676577 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Opioid prescription patterns and pain severity among patients with opioid use disorder and other substance use disorders: a mixed methods study.Pain Rep. 2025 Apr 18;10(3):e1261. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000001261. eCollection 2025 Jun. Pain Rep. 2025. PMID: 40291380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bounes V., Palmaro A., Lapeyre-Mestre M., Roussin A. Long-term consequences of acute pain for patients under methadone or buprenorphine maintenance treatment. Pain Phys. 2013;16:E739–E747. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) National Center For Injury Prevention and Control, Division of Unintentional Injury Prevention; Atlanta, GA: 2018. Quality Improvement and Care Coordination: Implementing the CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids For Chronic Pain.
-
- Ditre J.W., Zale E.L., LaRowe L.R. A reciprocal model of pain and substance use: transdiagnostic considerations, clinical implications, and future directions. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2019;15:503–528. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources