The oncogenic and immunological roles of histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 in human cancers and their experimental validation in the MCF-7 cell line
- PMID: 36846002
- PMCID: PMC9951023
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-6637
The oncogenic and immunological roles of histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 in human cancers and their experimental validation in the MCF-7 cell line
Abstract
Background: Histidine triad nucleotide binding protein 1 (HINT1) is a haplo-insufficient tumor suppressor gene that plays a significant role in cell proliferation and survival. However, to date, no systematic pan-cancer analysis has been conducted to explore its function in prognosis, and its oncogenic and immunological roles. We also analyzed the role of HINT1 in breast cancer (BC) progression in vitro.
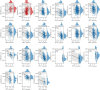
Methods: An analysis of the HINT1 expression pattern was performed using the TIMER database. The infiltration of immune cells into several cancer types was also studied using the Xena Shiny tool. To determine the relationship between stemness and the expression of HINT1 mRNA, the Spearman correlation test was used with the SangerBox tool. The correlation between HINT1 and functional states in various cancers was determined from the CancerSEA database. The potential role of HINT1 in BC oncogenesis was also investigated by Western blot and Annexin V/PI assays.
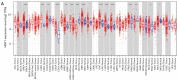
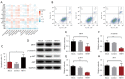
Results: The Cancer Genome Atlas pan-cancer data analysis suggested that HINT1 was extensively altered in most tumor tissues but not in most adjacent normal tissues. A high expression of HINT1 was associated with the decreased infiltration of cluster of differentiation (CD)4+ T cells. Importantly, increased HINT1 expression was also associated with a large majority of tumors with high stemness and lower stromal, immune, and estimate scores. Further, the expression of HINT1 was significantly associated with the tumor mutational burden (TMB) and microsatellite instability (MSI) in certain tumor types. Finally, HINT1 overexpression was found to impair BC progression by promoting cell apoptosis. HINT1 upregulation also reduced the expression of microphthalmia transcription factor (MITF) and β-catenin in BC Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 (MCF-7) cells, and the phosphorylation of protein kinase B (p-Akt).
Conclusions: The present study showed that HINT1 plays an oncogenic role in various cancers and could also be used as a biomarker for BC.
Keywords: Histidine triad nucleotide binding protein 1 (HINT1); apoptosis; breast cancer (BC); oncogenic role; tumor microenvironment.
2023 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-6637/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
