Dexmedetomidine ameliorates ischemia-induced nerve injury by up-regulating Sox11 expression
- PMID: 36846013
- PMCID: PMC9951012
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-6639
Dexmedetomidine ameliorates ischemia-induced nerve injury by up-regulating Sox11 expression
Abstract
Background: Dexmedetomidine (Dex) is associated with several biological processes. Ischemic stroke has the characteristics of high morbidity and mortality. Herein, we aimed to explore whether Dex ameliorates ischemia-induced injury and determine its mechanism.
Methods: Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blotting were used to measure gene and protein expression. Cellular viability and proliferation were assessed by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) assays, respectively. Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. An oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation model of SK-N-SH and SH-SY5Y cells was constructed. A middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model was also built to assess Dex function in vivo. Neuronal function was assessed using the Bederson Behavior Score and Longa Behavior Score.
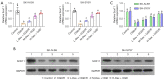
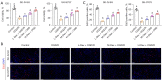
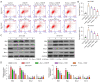
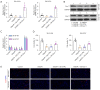
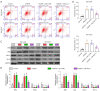
Results: We found that Dex positively and dose-dependently regulated Sox11 expression and prevented damage caused by oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R), enhancing cell viability and proliferation and reducing apoptosis in SK-N-SH and SH-SY5Y cells. The overexpression of Sox11 antagonized OGD/R-induced SK-N-SH and SH-SY5Y cell apoptosis and promoted cell growth in vitro. Furthermore, cell proliferation was decreased and cell apoptosis was increased after Sox11 knockdown in Dex-treated SK-N-SH and SH-SY5Y cells. We demonstrated that Dex prevented OGD/R-induced cell injury by up-regulating Sox11. Furthermore, we also confirmed that Dex protected rat from ischemia-induced injury in the MCAO model.
Conclusions: The role of Dex in cell viability and survival was verified in this study. Moreover, Dex protected neurons from MCAO-induced injury by up-regulating the expression of Sox11. Our research proposes a potential drug to improve the functional recovery of stroke patients in the clinic.
Keywords: Ischemic stroke; Sox11; dexmedetomidine (Dex); middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO); oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R).
2023 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-6639/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Circ_0000647 promotes cell injury by modulating miR-126-5p/TRAF3 axis in oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced SK-N-SH cell model.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Mar;104:108464. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108464. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35021128
-
MiR-29b expression is associated with a dexmedetomidine-mediated protective effect against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury to SK-N-SH cells in vitro.Cell Biol Int. 2018 Mar;42(3):344-352. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10906. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Cell Biol Int. 2018. PMID: 29087603
-
Dexmedetomidine improves oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) -induced neurological injury through regulating SNHG11/miR-324-3p/VEGFA axis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):4794-4804. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1957071. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34334080 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-665 Participates in the Protective Effect of Dexmedetomidine in Ischemic Stroke by ROCK2/NF-κB Axis.Neurochem Res. 2022 Jul;47(7):2064-2075. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03597-x. Epub 2022 May 10. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35538293
-
Suppression of cerebral ischemia injury induced blood brain barrier breakdown by dexmedetomidine via promoting CCN1.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Feb 15;16(4):3750-3762. doi: 10.18632/aging.205557. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38364236 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Circ_0059662 exerts a positive role in oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced SK-N-SH cell injury.Exp Brain Res. 2023 Dec;241(11-12):2705-2714. doi: 10.1007/s00221-023-06714-6. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Exp Brain Res. 2023. PMID: 37815551
-
DeSUMOylation of IGF2BP2 Promotes Neuronal Differentiation of OM-MSCs by Stabilizing SOX11 to Ameliorate Brain Injury After Intracerebral Hemorrhage.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Jun;31(6):e70463. doi: 10.1111/cns.70463. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40485217 Free PMC article.
-
Progress on the Mechanisms and Neuroprotective Benefits of Dexmedetomidine in Brain Diseases.Brain Behav. 2024 Nov;14(11):e70116. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70116. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 39482839 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
