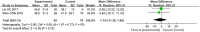Effects of physical activity on lung function and quality of life in asthmatic children: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36846162
- PMCID: PMC9944457
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2023.1074429
Effects of physical activity on lung function and quality of life in asthmatic children: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: The benefits of physical activity (PA) for asthmatic children were increasingly recognized, and as the design of studies on PA and asthma has become more refined in recent years, the latest evidence needed to be updated. We performed this meta-analysis to synthesize the evidence available from the last 10 years to update the effects of PA in asthmatic children.
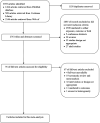
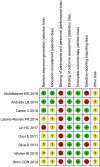
Methods: A systematic search was conducted in three databases, PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library. Randomized controlled trials were included, and two reviewers independently conducted the inclusion screening, data extraction, and bias assessment.
Results: A total of 9 studies were included in this review after 3,919 articles screened. PA significantly improved the forced vital capacity (FVC) (MD 7.62; 95% CI: 3.46 to 11.78; p < 0.001), and forced expiratory flow between 25% and 75% of forced vital capacity (FEF25-75) (MD 10.39; 95% CI: 2.96 to 17.82; p = 0.006) in lung function. There was no significant difference in forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1) (MD 3.17; 95% CI: -2.82 to 9.15; p = 0.30) and fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) (MD -1.74; 95% CI: -11.36 to 7.88; p = 0.72). Also, PA significantly improved the quality of life as assessed by the Pediatric Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (all items p < 0.05).
Conclusions: This review suggested that PA could improve FVC, FEF25-75, and quality of life in asthmatic children, but there was insufficient evidence of improvement in FEV1 and airway inflammation.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier: CRD42022338984.
Keywords: asthma; children; lung function; physical activity; quality of life.
© 2023 Jing, Wang, Zhang, Huang, Jia, Zhang, Wu and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation in Children With Asthma: A Meta-Analysis.Front Pediatr. 2022 Jun 29;10:840617. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.840617. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35844729 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of inspiratory muscle training in children with asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pediatr. 2024 Mar 18;12:1367710. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1367710. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38562138 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of exercise-based pulmonary rehabilitation on adults with asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Respir Res. 2021 Jan 30;22(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01627-w. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 33516207 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of continuous aerobic exercise on lung function and quality of life with asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Thorac Dis. 2020 Sep;12(9):4781-4795. doi: 10.21037/jtd-19-2813. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 33145051 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of exercise therapy for children with asthma: a meta-analysis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jul 10;11:1192929. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1192929. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37492220 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pulmonary function in swimmers exposed to disinfection by-products: a narrative review.Front Physiol. 2025 Jan 6;15:1473302. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1473302. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39835195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of the pediatric patient with asthma and obesity.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024 Jan;132(1):30-39. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2023.10.001. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37827386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effectiveness of physical activity in asthma management: An overview of systematic reviews.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 3;20(7):e0325488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325488. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40608793 Free PMC article.
-
The association between physical activity and lung function in adolescents: a cross-sectional NHANES study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 3;12:1538221. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1538221. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40529127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 2022 GINA MAIN REPORT. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention (2022). Available at: https://www.ginasthma.org/gina-reports (Accessed July 26, 2022).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources