Time-Series Forecasting of Hemodialysis Population in the State of Qatar by 2030
- PMID: 36846274
- PMCID: PMC9943994
- DOI: 10.5339/qmj.2023.6
Time-Series Forecasting of Hemodialysis Population in the State of Qatar by 2030
Abstract
Background: There are few statistics on dialysis-dependent individuals with end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) in Qatar. Having access to this information can aid in better understanding the dialysis development model, aiding higher-level services in future planning. In order to give data for creating preventive efforts, we thus propose a time-series with a definitive endogenous model to predict ESKD patients requiring dialysis.
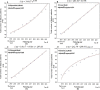
Methods: In this study, we used four mathematical equations linear, exponential, logarithmic decimal, and polynomial regression, to make predictions using historical data from 2012 to 2021. These equations were evaluated based on time-series analysis, and their prediction performance was assessed using the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), coefficient of determination (R2), and mean absolute deviation (MAD). Because it remained largely steady for the population at risk of ESKD in this investigation, we did not consider the population growth factor to be changeable. (FIFA World Cup 2022 preparation workforce associated growth was in healthy and young workers that did not influence ESKD prevalence).
Result: The polynomial has a high R2 of 0.99 and is consequently the best match for the prevalence dialysis data, according to numerical findings. Thus, the MAPE is 2.28, and the MAD is 9.87%, revealing a small prediction error with good accuracy and variability. The polynomial algorithm is the simplest and best-calculated projection model, according to these results. The number of dialysis patients in Qatar is anticipated to increase to 1037 (95% CI, 974-1126) in 2022, 1245 (95% CI, 911-1518) in 2025, and 1611 (95% CI, 1378-1954) in 2030, with a 5.67% average yearly percentage change between 2022 and 2030.
Conclusion: Our research offers straightforward and precise mathematical models for predicting the number of patients in Qatar who will require dialysis in the future. We discovered that the polynomial technique outperformed other methods. Future planning for the need for dialysis services can benefit from this forecasting.
Keywords: Chronic Kidney Disease; Dialysis; Forecasting; Hemodialysis; Prediction; Prevalence. Model. Trends; Qatar; Times series.
© 2023 Hamad, Al Halabi, Ghazouani, Habas, Borham, Ismail, Al-Malki, Alkadi, licensee HBKU Press.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hemodialysis delivery, dialysis dose achievement, and vascular access types in hemodialysis patients from the Gulf Cooperation Council countries enrolled in the dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study phase 5 (2012-2015).Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2016 Nov;27(6 Suppl 1):S42-50. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.194889. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2016. PMID: 27991478
-
Short and Long term predictions of Hospital emergency department attendances.Int J Med Inform. 2019 Sep;129:167-174. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.05.011. Epub 2019 May 13. Int J Med Inform. 2019. PMID: 31445251
-
Continuous urea monitoring in hemodialysis: a model approach to forecast dialytic performance. Results of a multicenter study.J Nephrol. 2001 Nov-Dec;14(6):481-7. J Nephrol. 2001. PMID: 11783604 Clinical Trial.
-
Population risk factors and trends in health care and public policy.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012 Mar;112(3 Suppl):S35-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2011.12.011. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012. PMID: 22709860 Review.
-
Prevalence and incidence of chronic kidney disease stage G5 in Japan.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2015 Feb;19(1):54-64. doi: 10.1007/s10157-014-0978-x. Epub 2014 May 13. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 24821288 Review.
Cited by
-
Severe acute respiratory infections: An epidemiological analysis of surveillance data in Bahrain, 2018-2022.Qatar Med J. 2024 Jul 1;2024(3):28. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2024.28. eCollection 2024. Qatar Med J. 2024. PMID: 38974774 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of vaccine adherence among non-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients in Qatar.Qatar Med J. 2024 Jan 6;2023(4):33. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2023.33. eCollection 2023. Qatar Med J. 2024. PMID: 38187993 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular calcification in hemodialysis patients: A Qatar-based prevalence and risk factors study.Qatar Med J. 2024 Mar 14;2024(1):18. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2024.18. eCollection 2024. Qatar Med J. 2024. PMID: 38654817 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Distance, Time, and Nonspatial Factors on Hemodialysis Access in Qatar.Cureus. 2024 Apr 18;16(4):e58569. doi: 10.7759/cureus.58569. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38765365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shigidi MM, Ramachandiran G, Rashed AH, Fituri OM. Demographic data and hemodialysis population dynamics in Qatar: A five year survey. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2009;20((3):):493-500. PMID: 19414963. - PubMed
-
- Vachharajani T, Jasuja S, AlSahow A, Alghamdi SMG, Al-Aradi AH, Al Salmi, I, et al. Current status and future of end-stage kidney disease in gulf cooperation council countries: Challenges and opportunities. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2021;32((4):):1073-10881. - PubMed
-
- AlSahow A, AlRukhaimi M, Al Wakeel J, Al-Ghamdi SM, AlGhareeb S, AlAli F et al. Demographics and key clinical characteristics of hemodialysis patients from the gulf cooperation council countries enrolled in the dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study phase 5 (2012-2015) Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2016;;27((6) (Suppl. 1):):S12-S23. - PubMed
-
- Data Commons: Place Explorer, country of Qatar. (Data from datacatalog.worldbank.org): Available online: https://datacommons.org/place/country/QAT?utm_medium=explore&mprop=count.... Available online: https://datacommons.org. (accessed in July 2022)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
